The Drosophila STUbL protein Degringolade limits HES functions during embryogenesis
- PMID: 21486924
- PMCID: PMC3074452
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.058420
The Drosophila STUbL protein Degringolade limits HES functions during embryogenesis
Abstract
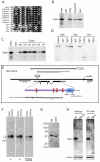
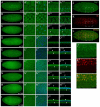
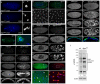
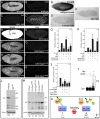
Degringolade (Dgrn) encodes a Drosophila SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase (STUbL) protein similar to that of mammalian RNF4. Dgrn facilitates the ubiquitylation of the HES protein Hairy, which disrupts the repressive activity of Hairy by inhibiting the recruitment of its cofactor Groucho. We show that Hey and all HES family members, except Her, interact with Dgrn and are substrates for its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Dgrn displays dynamic subcellular localization, accumulates in the nucleus at times when HES family members are active and limits Hey and HES family activity during sex determination, segmentation and neurogenesis. We show that Dgrn interacts with the Notch signaling pathway by it antagonizing the activity of E(spl)-C proteins. dgrn null mutants are female sterile, producing embryos that arrest development after two or three nuclear divisions. These mutant embryos exhibit fragmented or decondensed nuclei and accumulate higher levels of SUMO-conjugated proteins, suggesting a role for Dgrn in genome stability.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Degringolade, a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase, inhibits Hairy/Groucho-mediated repression.EMBO J. 2011 Apr 6;30(7):1289-301. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.42. Epub 2011 Feb 22. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21343912 Free PMC article.
-
A fly view of a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase.Fly (Austin). 2011 Oct-Dec;5(4):340-4. doi: 10.4161/fly.5.4.17608. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Fly (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21857164
-
The Biology of SUMO-Targeted Ubiquitin Ligases in Drosophila Development, Immunity, and Cancer.J Dev Biol. 2018 Jan 1;6(1):2. doi: 10.3390/jdb6010002. J Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29615551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase, Dgrn, is essential for Drosophila innate immunity.Int J Dev Biol. 2017;61(3-4-5):319-327. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.160250ao. Int J Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28621429
-
E(spl): genetic, developmental, and evolutionary aspects of a group of invertebrate Hes proteins with close ties to Notch signaling.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014;110:217-62. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-405943-6.00006-3. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25248478 Review.
Cited by
-
Notch-Dependent Expression of the Drosophila Hey Gene Is Supported by a Pair of Enhancers with Overlapping Activities.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 14;15(8):1071. doi: 10.3390/genes15081071. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202431 Free PMC article.
-
RNF4~RGMb~BMP6 axis required for osteogenic differentiation and cancer cell survival.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Sep 24;13(9):820. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05262-1. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36153321 Free PMC article.
-
RASSF1A disrupts the NOTCH signaling axis via SNURF/RNF4-mediated ubiquitination of HES1.EMBO Rep. 2022 Feb 3;23(2):e51287. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051287. Epub 2021 Dec 13. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 34897944 Free PMC article.
-
From the Evasion of Degradation to Ubiquitin-Dependent Protein Stabilization.Cells. 2021 Sep 9;10(9):2374. doi: 10.3390/cells10092374. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila H2Av negatively regulates the activity of the IMD pathway via facilitating Relish SUMOylation.PLoS Genet. 2021 Aug 9;17(8):e1009718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009718. eCollection 2021 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34370736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams E. W., Vining M. S., Andrew D. J. (2003). Constructing an organ: the Drosophila salivary gland as a model for tube formation. Trends Cell Biol. 13, 247-254 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Saadon R., Zaaroor D., Ziv T., Ciechanover A. (2006). The polycomb protein Ring1B generates self atypical mixed ubiquitin chains required for its in vitro Histone H2A ligase activity. Mol. Cell 24, 701-711 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

