The Jasmonate-ZIM domain proteins interact with the R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB21 and MYB24 to affect Jasmonate-regulated stamen development in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 21447791
- PMCID: PMC3082250
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.111.083089
The Jasmonate-ZIM domain proteins interact with the R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB21 and MYB24 to affect Jasmonate-regulated stamen development in Arabidopsis
Abstract
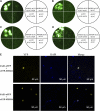
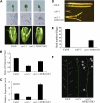
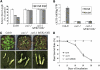
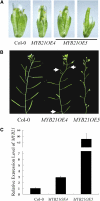
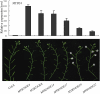
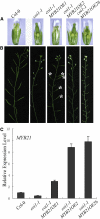
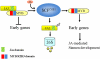
The Arabidopsis thaliana F-box protein CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1 (COI1) perceives jasmonate (JA) signals and subsequently targets the Jasmonate-ZIM domain proteins (JAZs) for degradation by the SCF(COI1)-26S proteasome pathway to mediate various jasmonate-regulated processes, including fertility, root growth, anthocyanin accumulation, senescence, and defense. In this study, we screened JAZ-interacting proteins from an Arabidopsis cDNA library in the yeast two-hybrid system. MYB21 and MYB24, two R2R3-MYB transcription factors, were found to interact with JAZ1, JAZ8, and JAZ11 in yeast and in planta. Genetic and physiological experiments showed that the myb21 myb24 double mutant exhibited defects specifically in pollen maturation, anther dehiscence, and filament elongation leading to male sterility. Transgenic expression of MYB21 in the coi1-1 mutant was able to rescue male fertility partially but unable to recover JA-regulated root growth inhibition, anthocyanin accumulation, and plant defense. These results demonstrate that the R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB21 and MYB24 function as direct targets of JAZs to regulate male fertility specifically. We speculate that JAZs interact with MYB21 and MYB24 to attenuate their transcriptional function; upon perception of JA signal, COI1 recruits JAZs to the SCF(COI1) complex for ubiquitination and degradation through the 26S proteasome; MYB21 and MYB24 are then released to activate expression of various genes essential for JA-regulated anther development and filament elongation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The DELLA proteins interact with MYB21 and MYB24 to regulate filament elongation in Arabidopsis.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Feb 7;20(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2274-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32033528 Free PMC article.
-
The Jasmonate-ZIM-domain proteins interact with the WD-Repeat/bHLH/MYB complexes to regulate Jasmonate-mediated anthocyanin accumulation and trichome initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell. 2011 May;23(5):1795-814. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.083261. Epub 2011 May 6. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21551388 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulators of stamen development in Arabidopsis identified by transcriptional profiling.Plant J. 2006 Jun;46(6):984-1008. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02756.x. Plant J. 2006. PMID: 16805732
-
Gibberellin and jasmonate crosstalk during stamen development.J Integr Plant Biol. 2009 Dec;51(12):1064-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2009.00881.x. J Integr Plant Biol. 2009. PMID: 20021553 Review.
-
The JAZ proteins: a crucial interface in the jasmonate signaling cascade.Plant Cell. 2011 Sep;23(9):3089-100. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.089300. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21963667 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamics of Jasmonate Metabolism upon Flowering and across Leaf Stress Responses in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plants (Basel). 2016 Jan 6;5(1):4. doi: 10.3390/plants5010004. Plants (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27135224 Free PMC article.
-
Social Network: JAZ Protein Interactions Expand Our Knowledge of Jasmonate Signaling.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Mar 8;3:41. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00041. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22629274 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of a 'Paulownia fortunei' MYB Factor Gene, PfMYB44, Increases Salt and Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 15;13(16):2264. doi: 10.3390/plants13162264. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204700 Free PMC article.
-
Survey of Genes Involved in Biosynthesis, Transport, and Signaling of Phytohormones with Focus on Solanum lycopersicum.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2016 Sep 26;10:185-207. doi: 10.4137/BBI.S38425. eCollection 2016. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2016. PMID: 27695302 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis identifies key gene LiMYB305 involved in monoterpene biosynthesis in Lilium 'Siberia'.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 7;13:1021576. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1021576. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36420028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baudry A., Caboche M., Lepiniec L. (2006). TT8 controls its own expression in a feedback regulation involving TTG1 and homologous MYB and bHLH factors, allowing a strong and cell-specific accumulation of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 46: 768–779 - PubMed
-
- Boavida L.C., McCormick S. (2007). Temperature as a determinant factor for increased and reproducible in vitro pollen germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 52: 570–582 - PubMed
-
- Browse J. (2009). Jasmonate passes muster: A receptor and targets for the defense hormone. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 60: 183–205 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

