MEK-ERK pathway modulation ameliorates disease phenotypes in a mouse model of Noonan syndrome associated with the Raf1(L613V) mutation
- PMID: 21339642
- PMCID: PMC3049402
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI44929
MEK-ERK pathway modulation ameliorates disease phenotypes in a mouse model of Noonan syndrome associated with the Raf1(L613V) mutation
Abstract
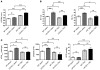
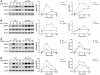
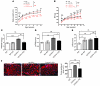
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a leading cause of sudden death in children and young adults. Abnormalities in several signaling pathways are implicated in the pathogenesis of HCM, but the role of the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK MAPK pathway has been controversial. Noonan syndrome (NS) is one of several autosomal-dominant conditions known as RASopathies, which are caused by mutations in different components of this pathway. Germline mutations in RAF1 (which encodes the serine-threonine kinase RAF1) account for approximately 3%-5% of cases of NS. Unlike other NS alleles, RAF1 mutations that confer increased kinase activity are highly associated with HCM. To explore the pathogenesis of such mutations, we generated knockin mice expressing the NS-associated Raf1(L613V) mutation. Like NS patients, mice heterozygous for this mutation (referred to herein as L613V/+ mice) had short stature, craniofacial dysmorphia, and hematologic abnormalities. Valvuloseptal development was normal, but L613V/+ mice exhibited eccentric cardiac hypertrophy and aberrant cardiac fetal gene expression, and decompensated following pressure overload. Agonist-evoked MEK-ERK activation was enhanced in multiple cell types, and postnatal MEK inhibition normalized the growth, facial, and cardiac defects in L613V/+ mice. These data show that different NS genes have intrinsically distinct pathological effects, demonstrate that enhanced MEK-ERK activity is critical for causing HCM and other RAF1-mutant NS phenotypes, and suggest a mutation-specific approach to the treatment of RASopathies.
Figures

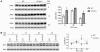
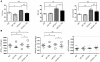
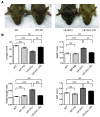
Comment in
-
RAS signaling pathway mutations and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: getting into and out of the thick of it.J Clin Invest. 2011 Mar;121(3):844-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI46399. Epub 2011 Feb 21. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21339640 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Cellular interplay via cytokine hierarchy causes pathological cardiac hypertrophy in RAF1-mutant Noonan syndrome.Nat Commun. 2017 May 26;8:15518. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15518. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28548091 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Reveal Aberrant Extracellular Regulated Kinase 5 and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 1/2 Signaling Concomitantly Promote Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in RAF1-Associated Noonan Syndrome.Circulation. 2019 Jul 16;140(3):207-224. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037227. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 31163979 Free PMC article.
-
RSK3 is required for concentric myocyte hypertrophy in an activated Raf1 model for Noonan syndrome.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Apr;93:98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.02.020. Epub 2016 Mar 3. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26940993 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2007 Apr;7(4):295-308. doi: 10.1038/nrc2109. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17384584 Review.
-
Noonan, Costello and cardio-facio-cutaneous syndromes: dysregulation of the Ras-MAPK pathway.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008 Dec 9;10:e37. doi: 10.1017/S1462399408000902. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 19063751 Review.
Cited by
-
Key role of ERK1/2 molecular scaffolds in heart pathology.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Nov;70(21):4047-54. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1321-5. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23532408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Report: Progressive central conducting lymphatic abnormalities in the RASopathies. Two case reports, including successful treatment by MEK inhibition.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 27;13:1001105. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1001105. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36238151 Free PMC article.
-
Functional robustness of adult spermatogonial stem cells after induction of hyperactive Hras.PLoS Genet. 2019 May 3;15(5):e1008139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008139. eCollection 2019 May. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31050682 Free PMC article.
-
Role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling underlying cardiac hypertrophy.Cardiol J. 2021;28(3):473-482. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2020.0061. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Cardiol J. 2021. PMID: 32329039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel therapeutic perspectives in Noonan syndrome and RASopathies.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Mar;183(3):1011-1019. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05263-y. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 37863846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heineke J, Molkentin JD. Regulation of cardiac hypertrophy by intracellular signalling pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(8):589–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

