Rapamycin blocks production of KSHV/HHV8: insights into the anti-tumor activity of an immunosuppressant drug
- PMID: 21264294
- PMCID: PMC3021514
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014535
Rapamycin blocks production of KSHV/HHV8: insights into the anti-tumor activity of an immunosuppressant drug
Abstract
Background: Infection with Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV8) often results in the development of fatal tumors in immunocompromised patients. Studies of renal transplant recipients show that use of the immunosuppressant drug rapamycin, an mTOR inhibitor, both prevents and can induce the regression of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), an opportunistic tumor that arises within a subset of this infected population. In light of rapamycin's marked anti-KS activity, we tested whether the drug might directly inhibit the KSHV life cycle. We focused on the molecular switch that triggers this predominantly latent virus to enter the lytic (productive) replication phase, since earlier work links this transition to viral persistence and tumorigenesis.
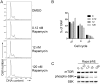
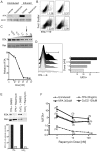
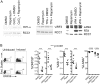
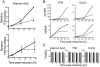
Methods and findings: In latently infected human B cell lines, we found that rapamycin inhibited entry of the virus into the lytic replication cycle, marked by a loss of expression of the lytic switch protein, replication and transcription activator (RTA). To test for viral-specific effects of rapamycin, we focused our studies on a B cell line with resistance to rapamycin-mediated growth inhibition. Using this line, we found that the drug had minimal effect on cell cycle profiles, cellular proliferation, or the expression of other cellular or latent viral proteins, indicating that the RTA suppression was not a result of global cellular dysregulation. Finally, treatment with rapamycin blocked the production of progeny virions.
Conclusions: These results indicate that mTOR plays a role in the regulation of RTA expression and, therefore, KSHV production, providing a potential molecular explanation for the marked clinical success of rapamycin in the treatment and prevention of post-transplant Kaposi's sarcoma. The striking inhibition of rapamycin on KSHV lytic replication, thus, helps explain the apparent paradox of an immunosuppressant drug suppressing the pathogenesis of an opportunistic viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glycolysis, Glutaminolysis, and Fatty Acid Synthesis Are Required for Distinct Stages of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Replication.J Virol. 2017 Apr 28;91(10):e02237-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02237-16. Print 2017 May 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28275189 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Replication Interferes with mTORC1 Regulation of Autophagy and Viral Protein Synthesis.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00854-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00854-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31375594 Free PMC article.
-
ARID3B: a Novel Regulator of the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Cycle.J Virol. 2016 Sep 29;90(20):9543-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03262-15. Print 2016 Oct 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27512077 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: the role of lytic replication in targeted therapy.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015 Dec;28(6):611-24. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000213. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26524334 Review.
-
[Replication Machinery of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus and Drug Discovery Research].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):69-73. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00164-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606932 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Kaposi Sarcoma.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017 Aug;18(4):529-539. doi: 10.1007/s40257-017-0270-4. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28324233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Kaposi Sarcoma in HIV-seronegative Saudi patient: Literature review and case report.Saudi Dent J. 2017 Jul;29(3):129-134. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 May 3. Saudi Dent J. 2017. PMID: 28725131 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of mTOR complexes in the kidney: implications for renal disease and transplantation.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Oct;12(10):587-609. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.108. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27477490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variable episomal silencing of a recombinant herpesvirus renders its encoded GFP an unreliable marker of infection in primary cells.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 17;9(11):e111502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111502. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25402328 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA quality control pathway nonsense-mediated mRNA decay targets cellular and viral RNAs to restrict KSHV.Nat Commun. 2020 Jul 3;11(1):3345. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17151-2. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32620802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Casper C, Nichols WG, Huang ML, Corey L, Wald A. Remission of HHV-8 and HIV-associated multicentric Castleman disease with ganciclovir treatment. Blood. 2004;103:1632–1634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

