Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade improves diastolic function independent of blood pressure reduction in a transgenic model of RAAS overexpression
- PMID: 21239636
- PMCID: PMC3075026
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01000.2010
Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade improves diastolic function independent of blood pressure reduction in a transgenic model of RAAS overexpression
Abstract
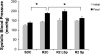
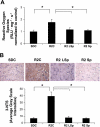
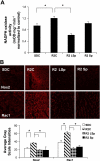
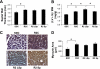
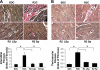
There is emerging evidence that aldosterone can promote diastolic dysfunction and cardiac fibrosis independent of blood pressure effects, perhaps through increased oxidative stress and inflammation. Accordingly, this investigation was designed to ascertain if mineralocorticoid receptor blockade improves diastolic dysfunction independently of changes in blood pressure through actions on myocardial oxidative stress and fibrosis. We used young transgenic (mRen2)27 [TG(mRen2)27] rats with increases in both tissue ANG II and circulating aldosterone, which manifests age-related increases in hypertension and cardiac dysfunction. Male TG(mRen2)27 and age-matched Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with either a low dose (∼1 mg·kg(-1)·day(-1)) or a vasodilatory, conventional dose (∼30 mg·kg(-1)·day(-1)) of spironolactone or placebo for 3 wk. TG(mRen2)27 rats displayed increases in systolic blood pressure and plasma aldosterone levels as well as impairments in left ventricular diastolic relaxation without changes in systolic function on cine MRI. TG(mRen2)27 hearts also displayed hypertrophy (left ventricular weight, cardiomyoctye hypertrophy, and septal wall thickness) as well as fibrosis (interstitial and perivascular). There were increases in oxidative stress in TG(mRen2)27 hearts, as evidenced by increases in NADPH oxidase activity and subunits as well as ROS formation. Low-dose spironolactone had no effect on systolic blood pressure but improved diastolic dysfunction comparable to a conventional dose. Both doses of spironolactone caused comparable reductions in ROS/3-nitrotryosine immunostaining and perivascular and interstitial fibrosis. These data support the notion mineralocorticoid receptor blockade improves diastolic dysfunction through improvements in oxidative stress and fibrosis independent of changes in systolic blood pressure.
Figures
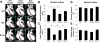
Similar articles
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade attenuates chronic overexpression of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system stimulation of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase and cardiac remodeling.Endocrinology. 2007 Aug;148(8):3773-80. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1691. Epub 2007 May 10. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17494996
-
Nebivolol improves diastolic dysfunction and myocardial remodeling through reductions in oxidative stress in the transgenic (mRen2) rat.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):H2341-51. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01126.2011. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22447938 Free PMC article.
-
Salt loading exacerbates diastolic dysfunction and cardiac remodeling in young female Ren2 rats.Metabolism. 2013 Dec;62(12):1761-71. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.08.010. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 24075738 Free PMC article.
-
[Spironolactone: renaissance of anti-aldosterone therapy in heart failure?].Praxis (Bern 1994). 1997 Apr 2;86(14):566-74. Praxis (Bern 1994). 1997. PMID: 9198851 Review. German.
-
Aldosterone and aldosterone antagonism in cardiovascular disease: focus on eplerenone (Inspra).Heart Dis. 2003 Mar-Apr;5(2):102-18. doi: 10.1097/01.hdx.0000061698.20666.aa. Heart Dis. 2003. PMID: 12713678 Review.
Cited by
-
Variable transcriptional regulation of the human aldosterone synthase gene causes salt-dependent high blood pressure in transgenic mice.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2015 Feb;8(1):30-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.114.000694. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2015. PMID: 25504670 Free PMC article.
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade prevents Western diet-induced diastolic dysfunction in female mice.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 May 1;308(9):H1126-35. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00898.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25747754 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mineralocorticoid receptor activation in cardiac diastolic dysfunction.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Aug;1863(8):2012-2018. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.10.025. Epub 2016 Oct 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 27989961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of low-dose spironolactone combined with irbesartan on cardiac hypertrophy induced by pressure overload in rats.Am J Transl Res. 2014 Nov 22;6(6):809-19. eCollection 2014. Am J Transl Res. 2014. PMID: 25628791 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of direct renin inhibition with angiotensin type 1 receptor blockade improves aldosterone but does not improve kidney injury in the transgenic Ren2 rat.Regul Pept. 2012 Jun 10;176(1-3):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2012.03.002. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Regul Pept. 2012. PMID: 22465166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brilla CG, Pick R, Tan LB, Janicki JS, Weber KT. Remodeling of the rat right and left ventricles in experimental hypertension. Circ Res 67: 1355– 1364, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Brilla CG, Weber KT. Reactive and reparative myocardial fibrosis in arterial hypertension in the rat. Cardiovasc Res 26: 671– 677, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Brilla CG, Zhou G, Matsubara L, Weber KT. Collagen metabolism in cultured adult rat cardiac fibroblasts: response to angiotensin II and aldosterone. J Mol Cell Cardiol 26: 809– 820, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Callera GE, Touyz RM, Tostes RC, Yogi A, He Y, Malkinson S, Schiffrin EL. Aldosterone activates vascular p38MAP kinase and NADPH oxidase via c-Src. Hypertension 45: 773– 779, 2005 - PubMed
-
- DeAngelis N, Fiordaliso F, Latini R, Calvillo L, Funicello M, Gobbi M, Mennini T, Masson S. Appraisal of the role of angiotensin II and aldosterone in ventricular myocyte apoptosis in adult normotensive rat. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34: 1655– 1665, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

