Silent information regulator 1 protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion
- PMID: 21060073
- PMCID: PMC3003297
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.958033
Silent information regulator 1 protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion
Abstract
Background: Silent information regulator 1 (Sirt1), a class III histone deacetylase, retards aging and protects the heart from oxidative stress. We here examined whether Sirt1 is protective against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R).
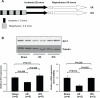
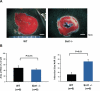
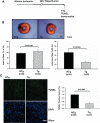
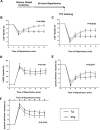
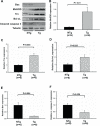
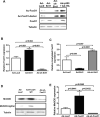
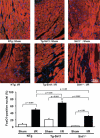
Methods and results: Protein and mRNA expression of Sirt1 is significantly reduced by I/R. Cardiac-specific Sirt1(-/-) mice exhibited a significant increase (44±5% versus 15±5%; P=0.01) in the size of myocardial infarction/area at risk. In transgenic mice with cardiac-specific overexpression of Sirt1, both myocardial infarction/area at risk (15±4% versus 36±8%; P=0.004) and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling-positive nuclei (4±3% versus 10±1%; P<0.003) were significantly reduced compared with nontransgenic mice. In Langendorff-perfused hearts, the functional recovery during reperfusion was significantly greater in transgenic mice with cardiac-specific overexpression of Sirt1 than in nontransgenic mice. Sirt1 positively regulates expression of prosurvival molecules, including manganese superoxide dismutase, thioredoxin-1, and Bcl-xL, whereas it negatively regulates the proapoptotic molecules Bax and cleaved caspase-3. The level of oxidative stress after I/R, as evaluated by anti-8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine staining, was negatively regulated by Sirt1. Sirt1 stimulates the transcriptional activity of FoxO1, which in turn plays an essential role in mediating Sirt1-induced upregulation of manganese superoxide dismutase and suppression of oxidative stress in cardiac myocytes. Sirt1 plays an important role in mediating I/R-induced increases in the nuclear localization of FoxO1 in vivo.
Conclusions: These results suggest that Sirt1 protects the heart from I/R injury through upregulation of antioxidants and downregulation of proapoptotic molecules through activation of FoxO and decreases in oxidative stress.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SIRT1 activation by curcumin pretreatment attenuates mitochondrial oxidative damage induced by myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:667-679. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23880291
-
Berberine Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Response: Role of Silent Information Regulator 1.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:1689602. doi: 10.1155/2016/1689602. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 26788242 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of Sirt1 as aging change in advanced heart failure.J Biomed Sci. 2014 Jun 9;21(1):57. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-21-57. J Biomed Sci. 2014. PMID: 24913149 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protection of the heart against ischemia/reperfusion by silent information regulator 1.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2011 Jan;21(1):27-32. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2012.01.005. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2011. PMID: 22498017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 is a regulator of autophagy: Implications for the progression and treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Jan;199:106957. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106957. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 37820856 Review.
Cited by
-
miRNAGE-34 induces cardiac damAGE.Cell Res. 2013 Jul;23(7):866-7. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.57. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23609795 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT Is Required for EDP-Mediated Protective Responses toward Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Injury in Cardiac Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2016 May 17;7:124. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00124. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27242531 Free PMC article.
-
Klotho inhibits IGF1R/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and protects the heart from oxidative stress during ischemia/reperfusion injury.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 20;13(1):20312. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47686-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37985893 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA 199a Is Downregulated in Patients After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery and Is Associated with Increased Levels of Sirtuin 1 (SIRT 1) Protein and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events at 3-Year Follow-Up.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Sep 7;24:6245-6254. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912065. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30192743 Free PMC article.
-
The sirtuin family in health and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Dec 29;7(1):402. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01257-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36581622 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M, Guarente L. Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature. 2000;403:795–800. - PubMed
-
- Howitz KT, Bitterman KJ, Cohen HY, Lamming DW, Lavu S, Wood JG, Zipkin RE, Chung P, Kisielewski A, Zhang LL, Scherer B, Sinclair DA. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature. 2003;425:191–196. - PubMed
-
- Tissenbaum HA, Guarente L. Increased dosage of a sir-2 gene extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2001;410:227–230. - PubMed
-
- Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K, Pistell PJ, Poosala S, Becker KG, Boss O, Gwinn D, Wang M, Ramaswamy S, Fishbein KW, Spencer RG, Lakatta EG, Le Couteur D, Shaw RJ, Navas P, Puigserver P, Ingram DK, de Cabo R, Sinclair DA. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature. 2006;444:337–342. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG023039-04/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027211/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-06/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-07/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028787/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL67724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102738-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-06/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG27211/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102738/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-08/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067727-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039-08/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027211-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091469/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028787-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091469-02W1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-10/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091469-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027211-02S1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039-07/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091469-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102738-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL69020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-08/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039-03/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139-06/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL91469/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-03S1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039-06S1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139-07/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL59139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027211-04/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027211-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139-10/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039-05/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102472/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091469-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027211-03/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069020-10/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139-08/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027211-05/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059139-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-11/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724-07/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091469-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039-06/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

