Induction of Sirt1 by mechanical stretch of skeletal muscle through the early response factor EGR1 triggers an antioxidative response
- PMID: 20971845
- PMCID: PMC3024751
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.149153
Induction of Sirt1 by mechanical stretch of skeletal muscle through the early response factor EGR1 triggers an antioxidative response
Abstract
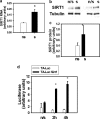
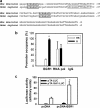
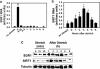
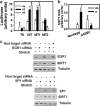
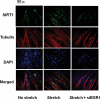
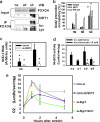
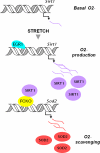
Mechanical loading of muscles by intrinsic muscle activity or passive stretch leads to an increase in the production of reactive oxygen species. The NAD-dependent protein deacetylase SIRT1 is involved in the protection against oxidative stress by enhancing FOXO-driven Sod2 transcription. In this report, we unravel a mechanism triggered by mechanical stretch of skeletal muscle cells that leads to an EGR1-dependent transcriptional activation of the Sirt1 gene. The resulting transient increase in SIRT1 expression generates an antioxidative response that contributes to reactive oxygen species scavenging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An autoregulatory loop reverts the mechanosensitive Sirt1 induction by EGR1 in skeletal muscle cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2012 Jul;4(7):456-61. doi: 10.18632/aging.100470. Aging (Albany NY). 2012. PMID: 22820707 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 1 attenuates oxidative stress via upregulation of superoxide dismutase 2 and catalase in astrocytes.J Neuroimmunol. 2014 Apr 15;269(1-2):38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Neuroimmunol. 2014. PMID: 24565075
-
SIRT1 is involved in glucocorticoid-mediated control of uncoupling protein-3 gene transcription.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 23;282(47):34066-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707114200. Epub 2007 Sep 20. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17884810
-
A systematic review of p53 regulation of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle.Redox Rep. 2018 Dec;23(1):100-117. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2017.1416773. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Redox Rep. 2018. PMID: 29298131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirt1 Inhibits Oxidative Stress in Vascular Endothelial Cells.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7543973. doi: 10.1155/2017/7543973. Epub 2017 May 4. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28546854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy of Stretching Exercises on Arterial Stiffness in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Non-Randomized Controlled Trials.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Aug 5;17(16):5643. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17165643. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32764418 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin Functions in Female Fertility: Possible Role in Oxidative Stress and Aging.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:659687. doi: 10.1155/2015/659687. Epub 2015 May 5. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26075037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissociation of increases in PGC-1α and its regulators from exercise intensity and muscle activation following acute exercise.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 12;8(8):e71623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071623. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951207 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of SIRT-1 in aging mice increases skeletal muscle fatigue by a PARP-1-dependent mechanism.Aging (Albany NY). 2014 Oct;6(10):820-34. doi: 10.18632/aging.100696. Aging (Albany NY). 2014. PMID: 25361036 Free PMC article.
-
The African killifish: A short-lived vertebrate model to study the biology of sarcopenia and longevity.Aging Cell. 2024 Jan;23(1):e13862. doi: 10.1111/acel.13862. Epub 2023 May 14. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 37183563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reid M. B., Durham W. J. (2002) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 959, 108–116 - PubMed
-
- Jackson M. J. (2008) Free Radic. Biol. Med. 44, 132–141 - PubMed
-
- van der Horst A., Tertoolen L. G., de Vries-Smits L. M., Frye R. A., Medema R. H., Burgering B. M. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 28873–28879 - PubMed
-
- Brunet A., Sweeney L. B., Sturgill J. F., Chua K. F., Greer P. L., Lin Y., Tran H., Ross S. E., Mostoslavsky R., Cohen H. Y., Hu L. S., Cheng H. L., Jedrychowski M. P., Gygi S. P., Sinclair D. A., Alt F. W., Greenberg M. E. (2004) Science 303, 2011–2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

