Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 potently induces apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells through a process regulated by endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 20858700
- PMCID: PMC2993469
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.110.068007
Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 potently induces apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells through a process regulated by endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
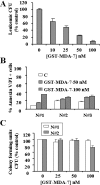
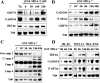
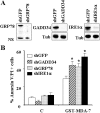
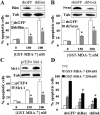
Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7 (mda-7)/interleukin-24 (IL-24), a member of the IL-10 cytokine gene family, preferentially induces cell death in neoplastic epithelial cells types while sparing their normal counterparts. The effects of mda-7/IL-24 in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells have not been extensively characterized. Treatment with recombinant GST-MDA-7/IL-24 potently induced apoptosis in diverse myeloid leukemia cell types including U937, HL60, MV4-11, EOL-1, and MLL/ENL cells. MDA-7/IL-24 also markedly induced apoptosis in and suppressed the colony-forming capacity of primary AML blasts but exerted minimal toxicity toward normal CD34(+) hematopoietic progenitor cells. MDA-7/IL-24 lethality was associated with pronounced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress induction in leukemia cell lines and primary AML blasts, manifested by the accumulation of growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 34 (GADD34), 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78)/BiP, inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α), and eukaryotic initiation factor 2α phosphorylation. It is noteworthy that short hairpin RNA (shRNA) knockdown of IRE1α, GADD34, or GRP78/BiP significantly enhanced MDA-7/IL-24-mediated apoptosis, indicating a protective role for these molecules against MDA-7/IL-24 lethality. MDA-7/IL-24 also down-regulated the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1 and sharply increased expression of the proapoptotic proteins Bim and Noxa. Ectopic Mcl-1 expression or shRNA knockdown of Bim or Noxa significantly attenuated MDA-7/IL-24-mediated leukemia cell death. Finally, knockdown of Bax or Bak significantly reduced MDA-7/IL-24 lethality. Together, these findings indicate that MDA-7/IL-24 potently induces apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells through a process regulated by ER stress induction, Mcl-1 down-regulation, and Bim and Noxa up-regulation. They also suggest that MDA-7/IL-24 warrants further investigation in myeloid leukemia.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cisplatin enhances protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase- and CD95-dependent melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7/interleukin-24-induced killing in ovarian carcinoma cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Feb;77(2):298-310. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.061820. Epub 2009 Nov 12. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19910452 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Bcl-2 antiapoptotic members by obatoclax potently enhances sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells through a Bim-dependent process.Blood. 2012 Jun 21;119(25):6089-98. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-378141. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22446485 Free PMC article.
-
Novel functions for mda-7/IL-24 and IL-24 delE5: regulation of differentiation of acute myeloid leukemic cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Apr;10(4):615-25. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0863. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21282359
-
Expression of FLT3 receptor and response to FLT3 ligand by leukemic cells.Leukemia. 1996 Apr;10(4):588-99. Leukemia. 1996. PMID: 8618433 Review.
-
Stem cell factor as a survival and growth factor in human normal and malignant hematopoiesis.Acta Haematol. 1996;95(3-4):257-62. doi: 10.1159/000203893. Acta Haematol. 1996. PMID: 8677752 Review.
Cited by
-
Dihydroarteminsin-induced apoptosis is not dependent on the translocation of Bim to the endoplasmic reticulum in human lung adenocarcinoma cells.Pathol Oncol Res. 2012 Oct;18(4):809-16. doi: 10.1007/s12253-012-9508-x. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Pathol Oncol Res. 2012. PMID: 22391963
-
Suppression of antitumor cytokine IL‑24 by PRG4 and PAI‑1 may promote myxoid liposarcoma cell survival.Biomed Rep. 2023 Jul 26;19(3):60. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1642. eCollection 2023 Sep. Biomed Rep. 2023. PMID: 37614985 Free PMC article.
-
PIKFYVE inhibitors trigger interleukin-24-dependent cell death of autophagy-dependent melanoma.Mol Oncol. 2024 Apr;18(4):988-1011. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13607. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38414326 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Termination of Autophagy-Dependent Cancers.Cells. 2024 Jun 25;13(13):1096. doi: 10.3390/cells13131096. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual inhibition of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL strikingly enhances PI3K inhibition-induced apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells through a GSK3- and Bim-dependent mechanism.Cancer Res. 2013 Feb 15;73(4):1340-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1365. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23243017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barabé F, Kennedy JA, Hope KJ, Dick JE. (2007) Modeling the initiation and progression of human acute leukemia in mice. Science 316:600–604 - PubMed
-
- Bernales S, Papa FR, Walter P. (2006) Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:487–508 - PubMed
-
- Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D. (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2:326–332 - PubMed
-
- Cnop M, Ladriere L, Hekerman P, Ortis F, Cardozo AK, Dogusan Z, Flamez D, Boyce M, Yuan J, Eizirik DL. (2007) Selective inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha dephosphorylation potentiates fatty acid-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and causes pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 282:3989–3997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
