Immunologic consequences of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 activation in human squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 20682796
- PMCID: PMC2922407
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4058
Immunologic consequences of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 activation in human squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
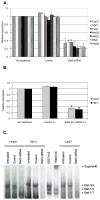
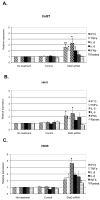
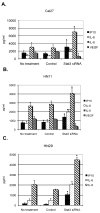
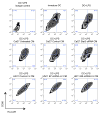
Paracrine cross-talk between tumor cells and immune cells within the tumor microenvironment underlies local mechanisms of immune evasion. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), which is constitutively activated in diverse cancer types, is a key regulator of cytokine and chemokine expression in murine tumors, resulting in suppression of both innate and adaptive antitumor immunity. However, the immunologic effects of STAT3 activation in human cancers have not been studied in detail. To investigate how STAT3 activity in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) might alter the tumor microenvironment to enable immune escape, we used small interfering RNA and small-molecule inhibitors to suppress STAT3 activity. STAT3 inhibition in multiple primary and established human squamous carcinoma lines resulted in enhanced expression and secretion of both proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Although conditioned medium containing supernatants from human HNSCC inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced dendritic cell activation in vitro, supernatants from STAT3-silenced tumor cells reversed this immune evasion mechanism. Moreover, supernatants from STAT3-silenced tumor cells were able to stimulate the migratory behavior of lymphocytes from human peripheral blood in vitro. These results show the importance of STAT3 activation in regulating the immunomodulatory mediators by human tumors and further validate STAT3 as a promising target for therapeutic intervention.
(c)2010 AACR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
STAT3 Induces Immunosuppression by Upregulating PD-1/PD-L1 in HNSCC.J Dent Res. 2017 Aug;96(9):1027-1034. doi: 10.1177/0022034517712435. Epub 2017 Jun 12. J Dent Res. 2017. PMID: 28605599 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor modulation in head and neck cancer.Crit Rev Immunol. 2008;28(3):201-13. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v28.i3.20. Crit Rev Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19024345 Review.
-
The role of STAT3 activation in modulating the immune microenvironment of GBM.J Neurooncol. 2012 Dec;110(3):359-68. doi: 10.1007/s11060-012-0981-6. Epub 2012 Oct 25. J Neurooncol. 2012. PMID: 23096132 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib up-regulates activated signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 and synergizes with inhibitors of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 to promote head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell death.Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Aug;8(8):2211-20. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0327. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19638453 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment.Nat Rev Immunol. 2007 Jan;7(1):41-51. doi: 10.1038/nri1995. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17186030 Review.
Cited by
-
Autologous reconstitution of human cancer and immune system in vivo.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):2053-2068. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14026. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28008146 Free PMC article.
-
Promising systemic immunotherapies in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2013 Dec;49(12):1089-96. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.09.009. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Oral Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24126223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Head and Neck Carcinoma Immunotherapy: Facts and Hopes.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jan 1;24(1):6-13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1261. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 28751445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid STAT3 promotes formation of colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice.Oncoimmunology. 2015 Jan 22;4(4):e998529. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2014.998529. eCollection 2015 Apr. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 26137415 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of apoptosis methods recently used in Cancer Research and Cell Death & Disease publications.Cell Death Dis. 2012 Feb 2;3(2):e263. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.2. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 22297295 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Yu H, Jove R. The STATs of cancer--new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(2):97–105. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE. Validating Stat3 in cancer therapy. Nat Med. 2005;11(6):595–6. - PubMed
-
- Nagpal JK, Mishra R, Das BR. Activation of stat-3 as one of the early events in tobacco chewing-mediated oral carcinogenesis. Cancer. 2002;94(9):2393–400. - PubMed
-
- Schust J, Sperl B, Hollis A, Mayer TU, Berg T. Stattic: A small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem Biol. 2006;13(11):1235–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

