Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- PMID: 20637991
- PMCID: PMC2908600
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncl.2010.03.003
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Abstract
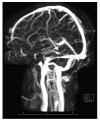
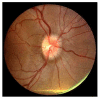
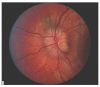
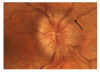
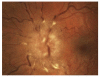
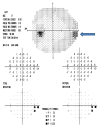
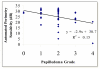
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension ((IIH) is characterized by increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure of unknown cause. It is predominantly a disease of women in the childbearing years. Although the cause of IIH remains obscure, it has become clear that loss of visual function is common and patients may progress to blindness if untreated. Diagnosis should adhere to the modified Dandy criteria and other causes of intracranial hypertension sought. IIH patient management should include serial perimetry and optic disc grading or photography. The proper therapy can then be selected and visual loss prevented or reversed. Although there are no evidence-based data to guide therapy, there is an ongoing randomized double-blind controlled treatment trial of IIH investigating diet and medical therapy.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
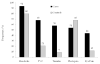



Similar articles
-
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension.Neurol Clin. 1991 Feb;9(1):73-95. Neurol Clin. 1991. PMID: 2011112 Review.
-
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension.Semin Ophthalmol. 1995 Sep;10(3):251-9. doi: 10.3109/08820539509060979. Semin Ophthalmol. 1995. PMID: 10159750 Review.
-
[Treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 11;52(12):948-951. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2016.12.016. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27998460 Review. Chinese.
-
The Pseudotumor Cerebri Syndrome.Neurol Clin. 2024 May;42(2):433-471. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2024.02.001. Neurol Clin. 2024. PMID: 38575259 Review.
-
[Idiopathic intracranial hypertension].Nervenarzt. 2017 Feb;88(2):191-200. doi: 10.1007/s00115-016-0279-6. Nervenarzt. 2017. PMID: 28083688 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Optic nerve head quantification in idiopathic intracranial hypertension by spectral domain OCT.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036965. Epub 2012 May 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22615858 Free PMC article.
-
Neuro-Ophthalmological Manifestations after Intramuscular Medroxyprogesterone: A Forme Fruste of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension?Neurol Int. 2016 Sep 30;8(3):6132. doi: 10.4081/ni.2016.6132. eCollection 2016 Sep 30. Neurol Int. 2016. PMID: 27761224 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Termination of Pregnancy Precipitating Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023 Nov-Dec;26(6):1042-1044. doi: 10.4103/aian.aian_770_23. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38229612 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Causes and Prognosis of Visual Acuity Loss at the Time of Initial Presentation in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Jun;56(6):3850-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16450. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26070058 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Study of Patient Engagement in the Treatment of a Chronic Disease.J Patient Exp. 2022 Apr 18;9:23743735221094088. doi: 10.1177/23743735221094088. eCollection 2022. J Patient Exp. 2022. PMID: 35465411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corbett JJ, Savino PJ, Thompson HS, et al. Visual loss in pseudotumor cerebri. Follow-up of 57 patients from five to 41 years and a profile of 14 patients with permanent severe visual loss. Arch Neurol. 1982;39:461–474. - PubMed
-
- Wall M, Hart WM, Jr., Burde RM. Visual field defects in idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) Am J Ophthalmol. 1983;96:654–669. - PubMed
-
- Corbett JJ, Mehta MP. Cerebrospinal fluid pressure in normal obese subjects and patients with pseudotumor cerebri. Neurology. 1983;33:1386–1388. - PubMed
-
- Smith JL. Whence pseudotumor cerebri? J Clin Neuro-ophthalmol. 1985;5:55–56. - PubMed
-
- Durcan FJ, Corbett JJ, Wall M. The incidence of pseudotumor cerebri. Population studies in Iowa and Louisiana. Arch Neurol. 1988;45:875–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

