PD-L1 has distinct functions in hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells in regulating T cell responses during chronic infection in mice
- PMID: 20551512
- PMCID: PMC2898584
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI40040
PD-L1 has distinct functions in hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells in regulating T cell responses during chronic infection in mice
Abstract
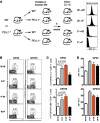
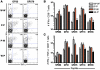
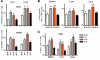
The inhibitory receptor programmed death 1 (PD-1) is upregulated on antigen-specific CD8+ T cells during persistent viral infections. Interaction with PD-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) contributes to functional exhaustion of responding T cells and may limit immunopathology during infection. PD-L1 is expressed on both hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells in tissues. However, the exact roles of PD-L1 on hematopoietic versus nonhematopoietic cells in modulating immune responses are unclear. Here we used bone marrow chimeric mice to examine the effects of PD-L1 deficiency in hematopoietic or nonhematopoietic cells during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus clone 13 (LCMV CL-13) infection. We found that PD-L1 expression on hematopoietic cells inhibited CD8+ T cell numbers and function after LCMV CL-13 infection. In contrast, PD-L1 expression on nonhematopoietic cells limited viral clearance and immunopathology in infected tissues. Together, these data demonstrate that there are distinct roles for PD-L1 on hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells in regulating CD8+ T cell responses and viral clearance during chronic viral infection.
Figures
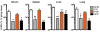
Similar articles
-
PD-L1 Checkpoint Inhibition Narrows the Antigen-Specific T Cell Receptor Repertoire in Chronic Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection.J Virol. 2020 Aug 31;94(18):e00795-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00795-20. Print 2020 Aug 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32641478 Free PMC article.
-
Aplastic anemia rescued by exhaustion of cytokine-secreting CD8+ T cells in persistent infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus.J Exp Med. 1998 Jun 1;187(11):1903-20. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.11.1903. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9607930 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between regulatory T cells and PD-1 in modulating T cell exhaustion and viral control during chronic LCMV infection.J Exp Med. 2014 Aug 25;211(9):1905-18. doi: 10.1084/jem.20132577. Epub 2014 Aug 11. J Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25113973 Free PMC article.
-
CD8 T cell dysfunction during chronic viral infection.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Aug;19(4):408-15. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.06.004. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17656078 Review.
-
IL-10: achieving balance during persistent viral infection.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2014;380:129-44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-43492-5_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25004816 Review.
Cited by
-
PD-1 promotes immune exhaustion by inducing antiviral T cell motility paralysis.J Exp Med. 2013 Apr 8;210(4):757-74. doi: 10.1084/jem.20121416. Epub 2013 Mar 25. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23530125 Free PMC article.
-
Differential CD4 T Regulatory Cell Phenotype Induced by Andes Hantavirus Glycoprotein.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Aug 25;10:430. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00430. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32984065 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic inflammation, immune escape, and oncogenesis in the liver: a unique neighborhood for novel intersections.Hepatology. 2012 Oct;56(4):1567-74. doi: 10.1002/hep.25674. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22378061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The majority of infiltrating CD8 T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis lesions is insensitive to enhanced PD-L1 levels on CNS cells.Glia. 2011 May;59(5):841-56. doi: 10.1002/glia.21158. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Glia. 2011. PMID: 21360758 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent Function of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Donor Tissue versus Recipient Immune System in a Murine Model of Bronchiolitis Obliterans.Am J Pathol. 2017 Jun;187(6):1368-1379. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Am J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28427861 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

