Antagonism of host antiviral responses by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus tegument protein ORF45
- PMID: 20485504
- PMCID: PMC2868026
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010573
Antagonism of host antiviral responses by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus tegument protein ORF45
Abstract
Virus infection of a cell generally evokes an immune response by the host to defeat the intruder in its effort. Many viruses have developed an array of strategies to evade or antagonize host antiviral responses. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is demonstrated in this report to be able to prevent activation of host antiviral defense mechanisms upon infection. Cells infected with wild-type KSHV were permissive for superinfection with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), suggesting that KSHV virions fail to induce host antiviral responses. We previously showed that ORF45, a KSHV immediate-early protein as well as a tegument protein of virions, interacts with IRF-7 and inhibits virus-mediated type I interferon induction by blocking IRF-7 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation (Zhu et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99:5573-5578, 2002). Here, using an ORF45-null recombinant virus, we demonstrate a profound role of ORF45 in inhibiting host antiviral responses. Infection of cells with an ORF45-null mutant recombinant KSHV (BAC-stop45) triggered an immune response that resisted VSV super-infection, concomitantly associated with appreciable increases in transcription of type I IFN and downstream anti-viral effector genes. Gain-of-function analysis showed that ectopic expression of ORF45 in human fibroblast cells by a lentivirus vector decreased the antiviral responses of the cells. shRNA-mediated silencing of IRF-7, that predominantly regulates both the early and late phase induction of type I IFNs, clearly indicated its critical contribution to the innate antiviral responses generated against incoming KSHV particles. Thus ORF45 through its targeting of the crucial IRF-7 regulated type I IFN antiviral responses significantly contributes to the KSHV survival immediately following a primary infection allowing for progression onto subsequent stages in its life-cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
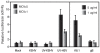
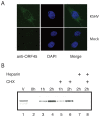

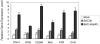

Similar articles
-
The ORF45 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is associated with purified virions.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(7):4221-30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.7.4221-4230.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12634379 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of autoinhibition of IRF-7 and a probable model for inactivation of IRF-7 by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus protein ORF45.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):746-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.150920. Epub 2010 Oct 27. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 20980251 Free PMC article.
-
ORF45 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus inhibits phosphorylation of interferon regulatory factor 7 by IKKε and TBK1 as an alternative substrate.J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(18):10162-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05224-11. Epub 2012 Jul 11. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22787218 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and the innate immune system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Oct;25(5):597-609. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.06.001. Epub 2014 Jun 21. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 25037686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ORF45 Protein of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus and Its Critical Role in the Viral Life Cycle.Viruses. 2022 Sep 11;14(9):2010. doi: 10.3390/v14092010. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reovirus Efficiently Reassorts Genome Segments during Coinfection and Superinfection.J Virol. 2022 Sep 28;96(18):e0091022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00910-22. Epub 2022 Sep 12. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36094315 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor sensing of human herpesvirus infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Oct 8;2:122. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00122. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23061052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein ICP0 is targeted by SIAH-1 for proteasomal degradation.J Virol. 2011 Aug;85(15):7644-57. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02207-10. Epub 2011 Jun 1. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21632771 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus open reading frame K8 by bacterial artificial chromosome-based mutagenesis.J Virol. 2011 Mar;85(5):1943-57. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02060-10. Epub 2010 Dec 15. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21159864 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV: pathways to tumorigenesis and persistent infection.Adv Virus Res. 2014;88:111-59. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800098-4.00002-7. Adv Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 24373311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Culpepper J, Knowles DM, et al. Identification of herpesvirus-loke DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865–1869. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1186–1191. - PubMed
-
- Soulier J, Grollet L, Okshendler E, Cacoub P, Cazals-Hatem D, et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood. 1995;86:1276–1280. - PubMed
-
- Goodbourn S, Didcock L, Randall RE. Interferons: cell signaling, immune modulation, antiviral response and virus countermeasures. J Gen Virol. 2000;81:2341–2364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

