Activation and repression of cellular immediate early genes by serum response factor cofactors
- PMID: 20466732
- PMCID: PMC2903344
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.108878
Activation and repression of cellular immediate early genes by serum response factor cofactors
Abstract
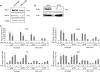
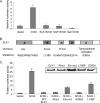
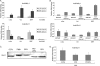
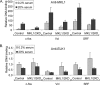
The induction of expression of many cellular immediate early genes (IEG) involves the transcription factor serum response factor (SRF). Two families of SRF coactivators have also been implicated in IEG induction, the ternary complex factors (TCFs), ELK1, Sap1, and Net, and the myocardin-related factors, MKL1 and MKL2. We found that serum induction of some SRF target genes is preferentially regulated by MKL1/2, whereas others are redundantly activated by both TCFs and MKL1/2. Yet ELK1 can also repress transcription. Binding of ELK1 and MKL1 to SRF has been found to be mutually exclusive in vitro, suggesting that ELK1 could repress expression of IEGs by blocking MKL1 binding. We characterized the in vivo binding of MKL1 and ELK1 to target genes and found an inverse relationship of serum-induced MKL1 binding and serum-decreased ELK1 binding. However, experiments with short hairpin RNA-mediated MKL1/2 depletion and expression of a nuclear MKL1 (N100) variant in stably transfected cells failed to alter ELK1 binding, suggesting that ELK1 binding to target genes is regulated independently of MKL1/2. Nevertheless, we found that short interfering RNA-mediated depletion of TCFs increased target gene expression in cells containing the N100 MKL1 activator, most notably in cells under continuous growth conditions. These results indicate that the TCFs can function both as activators and repressors of target gene expression depending upon the cellular growth conditions.
Figures
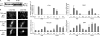
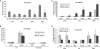
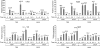
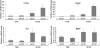
Similar articles
-
Megakaryoblastic leukemia 1, a potent transcriptional coactivator for serum response factor (SRF), is required for serum induction of SRF target genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Sep;23(18):6597-608. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.18.6597-6608.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12944485 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiling of serum inducible genes identifies a subset of SRF target genes that are MKL dependent.BMC Mol Biol. 2004 Aug 25;5:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-5-13. BMC Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15329155 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardin and ternary complex factors compete for SRF to control smooth muscle gene expression.Nature. 2004 Mar 11;428(6979):185-9. doi: 10.1038/nature02382. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15014501
-
Myocardin/MKL family of SRF coactivators: key regulators of immediate early and muscle specific gene expression.J Cell Biochem. 2004 Sep 1;93(1):74-82. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20199. J Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15352164 Review.
-
MKLs: co-factors of serum response factor (SRF) in neuronal responses.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Sep;44(9):1444-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.05.008. Epub 2012 May 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22626970 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytotoxic lymphocytes target characteristic biophysical vulnerabilities in cancer.Immunity. 2021 May 11;54(5):1037-1054.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.02.020. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Immunity. 2021. PMID: 33756102 Free PMC article.
-
Tenascin-C Promotes Tumor Cell Migration and Metastasis through Integrin α9β1-Mediated YAP Inhibition.Cancer Res. 2018 Feb 15;78(4):950-961. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1597. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29259017 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming progressive cells display low CAG promoter activity.Stem Cells. 2021 Jan;39(1):43-54. doi: 10.1002/stem.3295. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 33075202 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy proteins regulate ERK phosphorylation.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2799. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3799. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 24240988 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial and host determinants of MAL activation upon EPEC infection: the roles of Tir, ABRA, and FLRT3.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Apr;7(4):e1001332. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001332. Epub 2011 Apr 7. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21490959 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

