The Blimp1-Bcl6 axis is critical to regulate osteoclast differentiation and bone homeostasis
- PMID: 20368579
- PMCID: PMC2856022
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20091957
The Blimp1-Bcl6 axis is critical to regulate osteoclast differentiation and bone homeostasis
Abstract
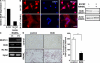
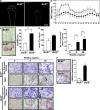
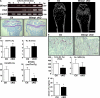
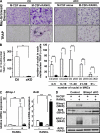
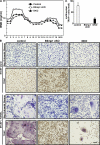
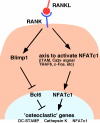
Controlling osteoclastogenesis is critical to maintain physiological bone homeostasis and prevent skeletal disorders. Although signaling activating nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 (NFATc1), a transcription factor essential for osteoclastogenesis, has been intensively investigated, factors antagonistic to NFATc1 in osteoclasts have not been characterized. Here, we describe a novel pathway that maintains bone homeostasis via two transcriptional repressors, B cell lymphoma 6 (Bcl6) and B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1 (Blimp1). We show that Bcl6 directly targets 'osteoclastic' molecules such as NFATc1, cathepsin K, and dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP), all of which are targets of NFATc1. Bcl6-overexpression inhibited osteoclastogenesis in vitro, whereas Bcl6-deficient mice showed accelerated osteoclast differentiation and severe osteoporosis. We report that Bcl6 is a direct target of Blimp1 and that mice lacking Blimp1 in osteoclasts exhibit osteopetrosis caused by impaired osteoclastogenesis resulting from Bcl6 up-regulation. Indeed, mice doubly mutant in Blimp1 and Bcl6 in osteoclasts exhibited decreased bone mass with increased osteoclastogenesis relative to osteoclast-specific Blimp1-deficient mice. These results reveal a Blimp1-Bcl6-osteoclastic molecule axis, which critically regulates bone homeostasis by controlling osteoclastogenesis and may provide a molecular basis for novel therapeutic strategies.
Figures
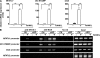
Similar articles
-
Agrimophol suppresses RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis through Blimp1-Bcl6 axis and prevents inflammatory bone loss in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jan;90:107137. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107137. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33199235
-
Ameloblastin attenuates RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis by suppressing activation of nuclear factor of activated T-cell cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1).J Cell Physiol. 2019 Feb;234(2):1745-1757. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27045. Epub 2018 Aug 13. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30105896
-
Regulators of osteoclast differentiation and cell-cell fusion.Keio J Med. 2011;60(4):101-5. doi: 10.2302/kjm.60.101. Keio J Med. 2011. PMID: 22200633 Review.
-
Unkeito Suppresses RANKL-Mediated Osteoclastogenesis via the Blimp1-Bcl6 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways and Enhancing Osteoclast Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 15;23(14):7814. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147814. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887169 Free PMC article.
-
[Suppressive effects for osteoclastogenesis regulated by RANKL signal].Clin Calcium. 2011 Aug;21(8):1141-7. Clin Calcium. 2011. PMID: 21814018 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Regulation of hematopoietic development by ZBTB transcription factors.Int J Hematol. 2016 Sep;104(3):310-23. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2035-x. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Int J Hematol. 2016. PMID: 27250345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in NFATC1 Signaling Pathway Genes and Susceptibility to Congenital Heart Disease in the Chinese Population.Pediatr Cardiol. 2016 Dec;37(8):1548-1561. doi: 10.1007/s00246-016-1469-5. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Pediatr Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27567908
-
miR-30b-5p inhibits osteoblast differentiation through targeting BCL6.Cell Cycle. 2022 Mar-Mar;21(6):630-640. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2031428. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Cell Cycle. 2022. PMID: 35100079 Free PMC article.
-
Britanin inhibits titanium wear particle‑induced osteolysis and osteoclastogenesis.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Nov;28(5):205. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13092. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37732549 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis and Osteoblastogenesis.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2023 Oct;38(5):504-521. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.501. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 37749800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baron B.W., Anastasi J., Thirman M.J., Furukawa Y., Fears S., Kim D.C., Simone F., Birkenbach M., Montag A., Sadhu A., et al. 2002. The human programmed cell death-2 (PDCD2) gene is a target of BCL6 repression: implications for a role of BCL6 in the down-regulation of apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99:2860–2865 10.1073/pnas.042702599 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cimmino L., Martins G.A., Liao J., Magnusdottir E., Grunig G., Perez R.K., Calame K.L. 2008. Blimp-1 attenuates Th1 differentiation by repression of ifng, tbx21, and bcl6 gene expression. J. Immunol. 181:2338–2347 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

