Evasion of CD8+ T cells is critical for superinfection by cytomegalovirus
- PMID: 20360110
- PMCID: PMC2883175
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1185350
Evasion of CD8+ T cells is critical for superinfection by cytomegalovirus
Abstract
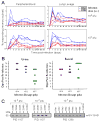
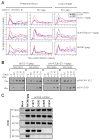
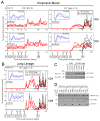
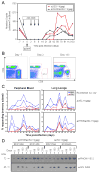
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) can superinfect persistently infected hosts despite CMV-specific humoral and cellular immunity; however, how it does so remains undefined. We have demonstrated that superinfection of rhesus CMV-infected rhesus macaques (RM) requires evasion of CD8+ T cell immunity by virally encoded inhibitors of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) antigen presentation, particularly the homologs of human CMV US2, 3, 6, and 11. In contrast, MHC-I interference was dispensable for primary infection of RM, or for the establishment of a persistent secondary infection in CMV-infected RM transiently depleted of CD8+ lymphocytes. These findings demonstrate that US2-11 glycoproteins promote evasion of CD8+ T cells in vivo, thus supporting viral replication and dissemination during superinfection, a process that complicates the development of preventive CMV vaccines but that can be exploited for CMV-based vector development.
Figures
Comment in
-
Virology. A vaccine monkey wrench?Science. 2010 Apr 2;328(5974):51-2. doi: 10.1126/science.1188578. Science. 2010. PMID: 20360096 No abstract available.
-
Viral immunity: How CMV bypasses immune memory.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 May;10(5):288. doi: 10.1038/nri2768. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20425915 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Virology. A vaccine monkey wrench?Science. 2010 Apr 2;328(5974):51-2. doi: 10.1126/science.1188578. Science. 2010. PMID: 20360096 No abstract available.
-
Human Macrophages Escape Inhibition of Major Histocompatibility Complex-Dependent Antigen Presentation by Cytomegalovirus and Drive Proliferation and Activation of Memory CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 May 25;9:1129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01129. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29887865 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses to cytomegalovirus in normal and simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques.J Virol. 1996 Nov;70(11):7725-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.11.7725-7733.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8892893 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the MHC class II antigen presentation pathway by human cytomegalovirus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002;269:101-15. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59421-2_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12224504 Review.
-
In vivo impact of cytomegalovirus evasion of CD8 T-cell immunity: facts and thoughts based on murine models.Virus Res. 2011 May;157(2):161-74. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.09.022. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20933556 Review.
Cited by
-
Rat Cytomegalovirus Vaccine Prevents Accelerated Chronic Rejection in CMV-Naïve Recipients of Infected Donor Allograft Hearts.Am J Transplant. 2015 Jul;15(7):1805-16. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13188. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Am J Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25766876 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of differential antiviral immunity in children and adults.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012 Sep;12(9):636-48. doi: 10.1038/nri3277. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22918466 Review.
-
Novel Human Cytomegalovirus Viral Chemokines, vCXCL-1s, Display Functional Selectivity for Neutrophil Signaling and Function.J Immunol. 2015 Jul 1;195(1):227-36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400291. Epub 2015 May 18. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25987741 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus persistence.Cell Microbiol. 2012 May;14(5):644-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01774.x. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22329758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of natural killer cell activity by viruses.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Aug;13(4):530-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.05.011. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20558100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P51 RR000163-486829/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007781/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000163-460222/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000163/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR00163/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059457-03/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 RR016001/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000163-508648/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059457-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR016025/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI021640/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI021640/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059457-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR016001/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U42 RR016025/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI060392/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR18107/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059457/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059457-01A2/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059457-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI040101/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000163-496081/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI021640-26/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 RR000163/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR018107/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040101/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

