Dual inhibition of PI3K and mTOR inhibits autocrine and paracrine proliferative loops in PI3K/Akt/mTOR-addicted lymphomas
- PMID: 20299510
- PMCID: PMC2881502
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-10-251082
Dual inhibition of PI3K and mTOR inhibits autocrine and paracrine proliferative loops in PI3K/Akt/mTOR-addicted lymphomas
Abstract
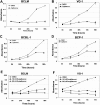
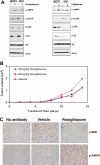
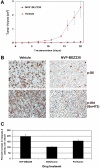
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) constitutes a subset of non-Hodgkin lymphoma whose incidence is highly increased in the context of HIV infection. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is the causative agent of PEL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway plays a critical role in cell proliferation and survival, and this pathway is dysregulated in many different cancers, including PEL, which display activated PI3K, Akt, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinases. PELs rely heavily on PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling, are dependent on autocrine and paracrine growth factors, and also have a poor prognosis with reported median survival times of less than 6 months. We compared different compounds that inhibit the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in PEL. Although compounds that modulated activity of only a single pathway member inhibited PEL proliferation, the use of a novel compound, NVP-BEZ235, that dually inhibits both PI3K and mTOR kinases was significantly more efficacious in culture and in a PEL xenograft tumor model. NVP-BEZ235 was effective at low nanomolar concentrations and has oral bioavailability. We also report a novel mechanism for NVP-BEZ235 involving the suppression of multiple autocrine and paracrine growth factors required for lymphoma survival. Our data have broad applicability for the treatment of cytokine-dependent tumors with PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
NVP-BEZ235, a novel dual PI3K-mTOR inhibitor displays anti-glioma activity and reduces chemoresistance to temozolomide in human glioma cells.Cancer Lett. 2015 Oct 10;367(1):58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 26188279
-
Genotype-dependent efficacy of a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, NVP-BEZ235, and an mTOR inhibitor, RAD001, in endometrial carcinomas.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37431. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037431. Epub 2012 May 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22662154 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of the novel dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 against osteosarcoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(4):602-9. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1017155. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25869769 Free PMC article.
-
Role of dual PI3/Akt and mTOR inhibition in Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia.Oncotarget. 2010 Nov;1(7):578-582. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.192. Oncotarget. 2010. PMID: 21317453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: current knowledge and clinical significance.Molecules. 2014 Sep 11;19(9):14304-15. doi: 10.3390/molecules190914304. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25215588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis in children with hematologic malignancies.Paediatr Drugs. 2012 Oct 1;14(5):299-316. doi: 10.2165/11594740-000000000-00000. Paediatr Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22845486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of mTOR inhibitor resistance in cancer therapy.Target Oncol. 2011 Mar;6(1):17-27. doi: 10.1007/s11523-011-0167-8. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Target Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21547705 Review.
-
Targeting xCT, a cystine-glutamate transporter induces apoptosis and tumor regression for KSHV/HIV-associated lymphoma.J Hematol Oncol. 2014 Apr 4;7:30. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-7-30. J Hematol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24708874 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of ESRRA in Endometrial Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:1533033821992083. doi: 10.1177/1533033821992083. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 33525981 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of fatty acid synthesis and glycolysis in non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 17;109(29):11818-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205995109. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22752304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature. 1995;378(6559):785–789. - PubMed
-
- Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, et al. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell. 1997;91(2):231–241. - PubMed
-
- del Peso L, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Page C, Herrera R, Nunez G. Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science. 1997;278(5338):687–689. - PubMed
-
- Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, et al. Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science. 1998;282(5392):1318–1321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA163217/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI045008/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DE018304/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018304-03/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- CA096500/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018304/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI045008/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA071341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA121947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018304-02/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018304-01/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA121947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32CA071341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA096500/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

