Mutations in the formin gene INF2 cause focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- PMID: 20023659
- PMCID: PMC2980844
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.505
Mutations in the formin gene INF2 cause focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Erratum in
- Nat Genet. 2010 Apr;42(4):361. Tonna, Stephen J [added]
Abstract
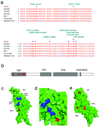
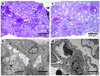
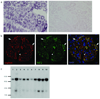
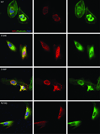
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a pattern of kidney injury observed either as an idiopathic finding or as a consequence of underlying systemic conditions. Several genes have been identified that, when mutated, lead to inherited FSGS and/or the related nephrotic syndrome. These findings have accelerated the understanding of glomerular podocyte function and disease, motivating our search for additional FSGS genes. Using linkage analysis, we identified a locus for autosomal-dominant FSGS susceptibility on a region of chromosome 14q. By sequencing multiple genes in this region, we detected nine independent nonconservative missense mutations in INF2, which encodes a member of the formin family of actin-regulating proteins. These mutations, all within the diaphanous inhibitory domain of INF2, segregate with FSGS in 11 unrelated families and alter highly conserved amino acid residues. The observation that alterations in this podocyte-expressed formin cause FSGS emphasizes the importance of fine regulation of actin polymerization in podocyte function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inverted formin 2 mutations with variable expression in patients with sporadic and hereditary focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis.Kidney Int. 2012 Jan;81(1):94-9. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.297. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 21866090 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in INF2 are a major cause of autosomal dominant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Feb;22(2):239-45. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010050518. Epub 2011 Jan 21. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21258034 Free PMC article.
-
Variable renal phenotype in a family with an INF2 mutation.Pediatr Nephrol. 2011 Jan;26(1):73-6. doi: 10.1007/s00467-010-1644-5. Epub 2010 Aug 28. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 20803156
-
Role of formin INF2 in human diseases.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jan;49(1):735-746. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06869-x. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34698992 Review.
-
The formin INF2 in disease: progress from 10 years of research.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Nov;77(22):4581-4600. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03550-7. Epub 2020 May 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32451589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Podocyte biology and pathogenesis of kidney disease.Annu Rev Med. 2013;64:357-66. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-050311-163340. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Annu Rev Med. 2013. PMID: 23190150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An mDia1-INF2 formin activation cascade facilitated by IQGAP1 regulates stable microtubules in migrating cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jun 1;27(11):1797-808. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-07-0489. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27030671 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mutations in the inverted formin 2 gene of Chinese families contribute to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.Kidney Int. 2015 Sep;88(3):593-604. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.106. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Kidney Int. 2015. PMID: 26039629
-
Pharmacological targeting of actin-dependent dynamin oligomerization ameliorates chronic kidney disease in diverse animal models.Nat Med. 2015 Jun;21(6):601-9. doi: 10.1038/nm.3843. Epub 2015 May 11. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25962121 Free PMC article.
-
A network of conserved formins, regulated by the guanine exchange factor EXC-5 and the GTPase CDC-42, modulates tubulogenesis in vivo.Development. 2016 Nov 15;143(22):4173-4181. doi: 10.1242/dev.141861. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Development. 2016. PMID: 27697907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaplan JM, et al. Mutations in ACTN4, encoding alpha-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet. 2000;24:251–256. - PubMed
-
- Winn MP, et al. A mutation in the TRPC6 cation channel causes familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Science. 2005;308:1801–1804. - PubMed
-
- Chhabra ES, Higgs HN. INF2 Is a WASP homology 2 motif-containing formin that severs actin filaments and accelerates both polymerization and depolymerization. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:26754–26767. - PubMed
-
- D'Agati VD, Fogo AB, Bruijn JA, Jennette JC. Pathologic classification of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a working proposal. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43:368–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK054931/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK54931/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054931-10A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK054931/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK073091/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK073091/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM069818/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM069818/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK080947/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054931-13/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK080947/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088826/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

