Allele-selective inhibition of mutant huntingtin by peptide nucleic acid-peptide conjugates, locked nucleic acid, and small interfering RNA
- PMID: 19796074
- PMCID: PMC3908448
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04975.x
Allele-selective inhibition of mutant huntingtin by peptide nucleic acid-peptide conjugates, locked nucleic acid, and small interfering RNA
Abstract
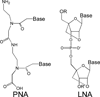
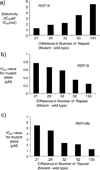
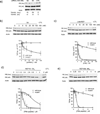
The ability to inhibit expression of a mutant allele while retaining expression of a wild-type protein might provide a useful approach to treating Huntington's Disease (HD) and other inherited pathologies. The mutant form of huntingtin (HTT), the protein responsible for HD, is encoded by an mRNA containing an expanded CAG repeat. We demonstrate that peptide nucleic acid conjugates and locked nucleic acids complementary to the CAG repeat selectively block expression of mutant HTT. The selectivity of inhibition is at least as good as that shown by a small interfering RNA targeted to a deletion polymorphism. Our data suggest that antisense oligomers are promising subjects for further development as an anti-HD therapeutic strategy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Allele-selective inhibition of mutant huntingtin expression with antisense oligonucleotides targeting the expanded CAG repeat.Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 30;49(47):10166-78. doi: 10.1021/bi101208k. Epub 2010 Nov 8. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 21028906 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-selective inhibition of huntingtin expression by switching to an miRNA-like RNAi mechanism.Chem Biol. 2010 Nov 24;17(11):1183-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.10.013. Chem Biol. 2010. PMID: 21095568 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-specific silencing of mutant huntingtin and ataxin-3 genes by targeting expanded CAG repeats in mRNAs.Nat Biotechnol. 2009 May;27(5):478-84. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1539. Epub 2009 May 3. Nat Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19412185 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic Acid Therapeutics in Huntington's Disease.Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2019;13(3):187-206. doi: 10.2174/1872208313666190208163714. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30747088 Review.
-
[Gene silencing approaches for the treatment of Huntington's disease].Med Sci (Paris). 2015 Feb;31(2):159-67. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20153102012. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Med Sci (Paris). 2015. PMID: 25744262 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Enhancing RNA inhibitory activity using clamp-G-modified nucleobases.Cell Rep Phys Sci. 2024 Aug 21;5(8):102120. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2024.102120. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Cell Rep Phys Sci. 2024. PMID: 39421604 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CAG repeat RNAs reduces Huntington's disease phenotype independently of huntingtin levels.J Clin Invest. 2016 Nov 1;126(11):4319-4330. doi: 10.1172/JCI83185. Epub 2016 Oct 10. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27721240 Free PMC article.
-
New directions in therapeutics for Huntington disease.Future Neurol. 2018 May;13(2):101-121. doi: 10.2217/fnl-2017-0035. Epub 2018 May 29. Future Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30800004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allele-specific suppression of mutant huntingtin using antisense oligonucleotides: providing a therapeutic option for all Huntington disease patients.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 10;9(9):e107434. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107434. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25207939 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide-mediated Cell and In Vivo Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides and siRNA.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2012 Jun 12;1(6):e27. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2012.18. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2012. PMID: 23344079 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Walker FO. Huntington’s disease. Lancet. 2007;369:218–228. - PubMed
-
- Gusella JF, MacDonald ME. Huntington’s disease: seeing the pathogenic process through a genetic lens. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006;31:533–540. - PubMed
-
- Duyao M, et al. Trinucleotide repeat length instability and age of onset in Huntington’s disease. Nat. Genet. 1993;4:387–392. - PubMed
-
- Kremer B, et al. A worldwide study of the Huntington’s disease mutation: The sensitivity and specificity of measuring CAG repeats. New Engl. J. Med. 1994;330:1401–1406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

