NF-kappaB p100 limits TNF-induced bone resorption in mice by a TRAF3-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 19770515
- PMCID: PMC2752069
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI38716
NF-kappaB p100 limits TNF-induced bone resorption in mice by a TRAF3-dependent mechanism
Abstract
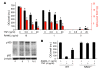
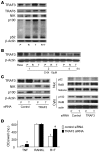
TNF and RANKL mediate bone destruction in common bone diseases, including osteoarthritis and RA. They activate NF-kappaB canonical signaling directly in osteoclast precursors (OCPs) to induce osteoclast formation in vitro. However, unlike RANKL, TNF does not activate the alternative NF-kappaB pathway efficiently to process the IkappaB protein NF-kappaB p100 to NF-kappaB p52, nor does it appear to induce osteoclast formation in vivo in the absence of RANKL. Here, we show that TNF limits RANKL- and TNF-induced osteoclast formation in vitro and in vivo by increasing NF-kappaB p100 protein accumulation in OCPs. In contrast, TNF induced robust osteoclast formation in vivo in mice lacking RANKL or RANK when the mice also lacked NF-kappaB p100, and TNF-Tg mice lacking NF-kappaB p100 had more severe joint erosion and inflammation than did TNF-Tg littermates. TNF, but not RANKL, increased OCP expression of TNF receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3), an adapter protein that regulates NF-kappaB p100 levels in B cells. TRAF3 siRNA prevented TNF-induced NF-kappaB p100 accumulation and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis. These findings suggest that upregulation of TRAF3 or NF-kappaB p100 expression or inhibition of NF-kappaB p100 degradation in OCPs could limit bone destruction and inflammation-induced bone loss in common bone diseases.
Figures
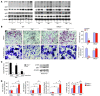
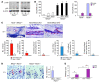
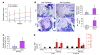
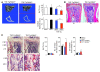
Comment in
-
NF-kappaB2 (p100) limits TNF-alpha-induced osteoclastogenesis.J Clin Invest. 2009 Oct;119(10):2879-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI40629. Epub 2009 Sep 21. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19770519 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Chloroquine reduces osteoclastogenesis in murine osteoporosis by preventing TRAF3 degradation.J Clin Invest. 2014 Jan;124(1):297-310. doi: 10.1172/JCI66947. Epub 2013 Dec 9. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24316970 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB2 (p100) limits TNF-alpha-induced osteoclastogenesis.J Clin Invest. 2009 Oct;119(10):2879-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI40629. Epub 2009 Sep 21. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19770519 Free PMC article.
-
TNF Induction of NF-κB RelB Enhances RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Promoting Inflammatory Macrophage Differentiation but also Limits It through Suppression of NFATc1 Expression.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 19;10(8):e0135728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135728. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26287732 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Remodeling and the Role of TRAF3 in Osteoclastic Bone Resorption.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 28;9:2263. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02263. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30323820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[NF-κB signaling pathways and the future perspectives of bone disease therapy using selective inhibitors of NF-κB].Clin Calcium. 2016 Feb;26(2):298-304. Clin Calcium. 2016. PMID: 26813510 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory bone resorption are inhibited by transcription factor RBP-J.J Exp Med. 2012 Feb 13;209(2):319-34. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111566. Epub 2012 Jan 16. J Exp Med. 2012. PMID: 22249448 Free PMC article.
-
TGFβ-induced degradation of TRAF3 in mesenchymal progenitor cells causes age-related osteoporosis.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 26;10(1):2795. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10677-0. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31243287 Free PMC article.
-
TNFα-mediated apoptosis in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes sensitized by PI3K-NF-κB inhibitor, not mTOR inhibitor.Rheumatol Int. 2012 Jul;32(7):2017-22. doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-1929-4. Epub 2011 Apr 9. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 21479603
-
RANKL-independent osteoclastogenesis in the SH3BP2 cherubism mice.Bone Rep. 2020 Mar 27;12:100258. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2020.100258. eCollection 2020 Jun. Bone Rep. 2020. PMID: 32258251 Free PMC article.
-
SH3BP2 cherubism mutation potentiates TNF-α-induced osteoclastogenesis via NFATc1 and TNF-α-mediated inflammatory bone loss.J Bone Miner Res. 2014 Dec;29(12):2618-35. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2295. J Bone Miner Res. 2014. PMID: 24916406 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

