Acute dasatinib exposure commits Bcr-Abl-dependent cells to apoptosis
- PMID: 19706883
- PMCID: PMC2765681
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-113969
Acute dasatinib exposure commits Bcr-Abl-dependent cells to apoptosis
Abstract
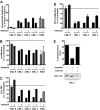
Pioneering work with the Bcr-Abl inhibitor, imatinib, demonstrated a requirement for constant Bcr-Abl inhibition to achieve maximal therapeutic benefit in treating chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), establishing a paradigm that has guided further drug development for this disease. Surprisingly, the second-generation Bcr-Abl inhibitor, dasatinib, was reported to be clinically effective with once-daily dosing, despite a short (3- to 5-hour) plasma half-life. Consistent with this observation, dasatinib treatment of progenitor cells from chronic-phase CML patients for 4 hours, followed by washout, or continuously for 72 hours both resulted in an induction of apoptosis and a reduction in the number of clonogenic cells. Such acute treatments with clinically achievable dasatinib concentrations also irreversibly committed Bcr-Abl+ CML cell lines to apoptotic cell death. Potent transient Bcr-Abl inhibition using the alternative inhibitor, nilotinib, also resulted in cell death. These findings demonstrate that in vitro assays designed to model in vivo pharmacokinetics can predict clinical efficacy. Furthermore, they challenge the widely held notion that continuous target inhibition is required for optimal efficacy of kinase inhibitors.
Figures
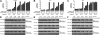
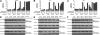
Similar articles
-
Threshold levels of ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors retained in chronic myeloid leukemia cells determine their commitment to apoptosis.Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 1;73(11):3356-70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3904. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23576564 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells transiently treated with imatinib or dasatinib is caused by residual BCR-ABL kinase inhibition.Am J Hematol. 2013 May;88(5):385-93. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23419. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Am J Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23420553
-
Cotreatment with vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid) enhances activity of dasatinib (BMS-354825) against imatinib mesylate-sensitive or imatinib mesylate-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Oct 1;12(19):5869-78. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0980. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17020995
-
The synthesis of Bcr-Abl inhibiting anticancer pharmaceutical agents imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib.Org Biomol Chem. 2013 Mar 21;11(11):1766-800. doi: 10.1039/c2ob27003j. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Org Biomol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23247657 Review.
-
Dasatinib: is it all in the dose?BioDrugs. 2010 Jun;24(3):157-63. doi: 10.2165/11535870-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2010. PMID: 20222756 Review.
Cited by
-
A screening-based approach to circumvent tumor microenvironment-driven intrinsic resistance to BCR-ABL+ inhibitors in Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Biomol Screen. 2014 Jan;19(1):158-67. doi: 10.1177/1087057113501081. Epub 2013 Aug 29. J Biomol Screen. 2014. PMID: 23989453 Free PMC article.
-
Novel approaches to treating advanced systemic mastocytosis.Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 10;11:77-92. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S206615. eCollection 2019. Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31372066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Response and Resistance to BCR-ABL1-Targeted Therapies.Cancer Cell. 2020 Apr 13;37(4):530-542. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.006. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32289275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What Is the Optimal Dose and Schedule for Dasatinib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Two Case Reports and Review of the Literature.Oncol Res. 2016 Jan 21;23(1-2):1-5. doi: 10.3727/096504015X14452563485986. Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 26802644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Threshold levels of ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors retained in chronic myeloid leukemia cells determine their commitment to apoptosis.Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 1;73(11):3356-70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3904. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23576564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rowley JD. A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining [letter]. Nature. 1973;243(5405):290–293. - PubMed
-
- Daley GQ, Van Etten RA, Baltimore D. Induction of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mice by the P210bcr/abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome. Science. 1990;247(4944):824–830. - PubMed
-
- Lugo TG, Pendergast AM, Muller AJ, Witte ON. Tyrosine kinase activity and transformation potency of bcr-abl oncogene products. Science. 1990;247(4946):1079–1082. - PubMed
-
- Buchdunger E, Zimmermann J, Mett H, et al. Inhibition of the Abl protein-tyrosine kinase in vitro and in vivo by a 2-phenylaminopyrimidine derivative. Cancer Res. 1996;56(1):100–104. - PubMed
-
- Shah NP, Tran C, Lee FY, Chen P, Norris D, Sawyers CL. Overriding imatinib resistance with a novel ABL kinase inhibitor. Science. 2004;305(5682):399–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

