Initiation of myoblast to brown fat switch by a PRDM16-C/EBP-beta transcriptional complex
- PMID: 19641492
- PMCID: PMC2754867
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08262
Initiation of myoblast to brown fat switch by a PRDM16-C/EBP-beta transcriptional complex
Abstract
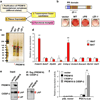
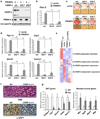
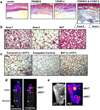
Brown adipose cells are specialized to dissipate chemical energy in the form of heat, as a physiological defence against cold and obesity. PRDM16 (PR domain containing 16) is a 140 kDa zinc finger protein that robustly induces brown fat determination and differentiation. Recent data suggests that brown fat cells arise in vivo from a Myf5-positive, myoblastic lineage by the action of PRDM16 (ref. 3); however, the molecular mechanisms responsible for this developmental switch is unclear. Here we show that PRDM16 forms a transcriptional complex with the active form of C/EBP-beta (also known as LAP), acting as a critical molecular unit that controls the cell fate switch from myoblastic precursors to brown fat cells. Forced expression of PRDM16 and C/EBP-beta is sufficient to induce a fully functional brown fat program in naive fibroblastic cells, including skin fibroblasts from mouse and man. Transplantation of fibroblasts expressing these two factors into mice gives rise to an ectopic fat pad with the morphological and biochemical characteristics of brown fat. Like endogenous brown fat, this synthetic brown fat tissue acts as a sink for glucose uptake, as determined by positron emission tomography with fluorodeoxyglucose. These data indicate that the PRDM16-C/EBP-beta complex initiates brown fat formation from myoblastic precursors, and may provide opportunities for the development of new therapeutics for obesity and type-2 diabetes.
Figures
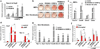
Similar articles
-
PRDM16 controls a brown fat/skeletal muscle switch.Nature. 2008 Aug 21;454(7207):961-7. doi: 10.1038/nature07182. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18719582 Free PMC article.
-
The engineering of brown fat.J Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;2(1):23-5. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjp035. Epub 2009 Oct 12. J Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19825852
-
EHMT1 controls brown adipose cell fate and thermogenesis through the PRDM16 complex.Nature. 2013 Dec 5;504(7478):163-7. doi: 10.1038/nature12652. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24196706 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PRDM16 in the activation of brown fat programming. Relevance to the development of obesity.Histol Histopathol. 2013 Nov;28(11):1411-25. doi: 10.14670/HH-28.1411. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Histol Histopathol. 2013. PMID: 23771475 Review.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of PRDM16: Adipose Biology and Beyond.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jan;27(1):11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26688472 Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of a doxycycline inducible adipogenic lentiviral expression system.Plasmid. 2013 Jan;69(1):96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Plasmid. 2013. PMID: 23099229 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting brown and beige adipocyte biogenesis through the PRDM16 pathway.Int J Obes Suppl. 2015 Aug;5(Suppl 1):S11-4. doi: 10.1038/ijosup.2015.4. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Int J Obes Suppl. 2015. PMID: 27152168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TSH promotes adiposity by inhibiting the browning of white fat.Adipocyte. 2020 Dec;9(1):264-278. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2020.1783101. Adipocyte. 2020. PMID: 32579056 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of VPS13C as a Galectin-12-Binding Protein That Regulates Galectin-12 Protein Stability and Adipogenesis.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 13;11(4):e0153534. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153534. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27073999 Free PMC article.
-
A novel therapeutic approach to treating obesity through modulation of TGFβ signaling.Endocrinology. 2012 Jul;153(7):3133-46. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1016. Epub 2012 May 1. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22549226 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- S10-RR-023010/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK087853/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK081605/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK031405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK081605/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067945/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG003456/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- GM67945/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK031405-28/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HG3456/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK31405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK081605/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK031405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023010/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

