Inhibition of osteoblastic bone formation by nuclear factor-kappaB
- PMID: 19448637
- PMCID: PMC2768554
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1954
Inhibition of osteoblastic bone formation by nuclear factor-kappaB
Abstract
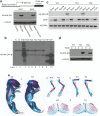
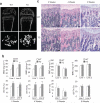
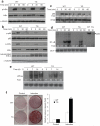
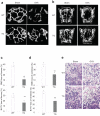
An imbalance in bone formation relative to bone resorption results in the net bone loss that occurs in osteoporosis and inflammatory bone diseases. Although it is well known how bone resorption is stimulated, the molecular mechanisms that mediate impaired bone formation are poorly understood. Here we show that the time- and stage-specific inhibition of endogenous inhibitor of kappaB kinase (IKK)--nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) in differentiated osteoblasts substantially increases trabecular bone mass and bone mineral density without affecting osteoclast activities in young mice. Moreover, inhibition of IKK-NF-kappaB in differentiated osteoblasts maintains bone formation, thereby preventing osteoporotic bone loss induced by ovariectomy in adult mice. Inhibition of IKK-NF-kappaB enhances the expression of Fos-related antigen-1 (Fra-1), an essential transcription factor involved in bone matrix formation in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, our results suggest that targeting IKK-NF-kappaB may help to promote bone formation in the treatment of osteoporosis and other bone diseases.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) inhibitor 4-IPP suppresses osteoclast formation and promotes osteoblast differentiation through the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway.FASEB J. 2019 Jun;33(6):7667-7683. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802364RR. Epub 2019 Mar 20. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30893559
-
Apolipoprotein E plays crucial roles in maintaining bone mass by promoting osteoblast differentiation via ERK1/2 pathway and by suppressing osteoclast differentiation via c-Fos, NFATc1, and NF-κB pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 5;503(2):644-650. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.055. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29906458
-
Suppression of NF-kappaB increases bone formation and ameliorates osteopenia in ovariectomized mice.Endocrinology. 2010 Oct;151(10):4626-34. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0399. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20810563
-
Novel functions for NFκB: inhibition of bone formation.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010 Oct;6(10):607-11. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.133. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20703218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of NF-κB in Physiological Bone Development and Inflammatory Bone Diseases: Is NF-κB Inhibition "Killing Two Birds with One Stone"?Cells. 2019 Dec 14;8(12):1636. doi: 10.3390/cells8121636. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31847314 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IFN-γ and TNF-α synergistically induce mesenchymal stem cell impairment and tumorigenesis via NFκB signaling.Stem Cells. 2013 Jul;31(7):1383-95. doi: 10.1002/stem.1388. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23553791 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical plasma concentration of vinpocetine does not affect osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Feb;73(1):202-210. doi: 10.1007/s43440-020-00153-8. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Pharmacol Rep. 2021. PMID: 32865810
-
[The Role of Histone Demethylase in Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Literature Review].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 May;52(3):364-372. doi: 10.12182/20210560202. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 34018352 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Endocrine sequelae of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Effects on mineral homeostasis and bone metabolism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 12;13:1085315. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1085315. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36714597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Tocotrienol in Preventing Male Osteoporosis-A Review of Current Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 18;20(6):1355. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061355. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30889819 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wagner EF, Karsenty G. Genetic control of skeletal development. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001;11:527–532. - PubMed
-
- Zaidi M. Skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Nat Med. 2007;13:791–801. - PubMed
-
- Zelzer E, Olsen BR. Multiple roles of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in skeletal development, growth, and repair. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005;65:169–187. - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg HM. Twist Genes Regulate Runx2 and Bone Formation. Dev. Cell. 2004;6:317–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DE016513/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE019412/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- DK053904/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DE019412/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE017684/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE019412-01/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE016513-06/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DE013848/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE017684-02/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- DE1016513/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- DE17684/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DE013848-10/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- E018890/PHS HHS/United States
- DE13848/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

