The significance of OX40 and OX40L to T-cell biology and immune disease
- PMID: 19426222
- PMCID: PMC2729757
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00766.x
The significance of OX40 and OX40L to T-cell biology and immune disease
Abstract
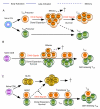
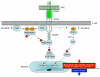
OX40 (CD134) and its binding partner, OX40L (CD252), are members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor/tumor necrosis factor superfamily and are expressed on activated CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells as well as on a number of other lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells. Costimulatory signals from OX40 to a conventional T cell promote division and survival, augmenting the clonal expansion of effector and memory populations as they are being generated to antigen. OX40 additionally suppresses the differentiation and activity of T-regulatory cells, further amplifying this process. OX40 and OX40L also regulate cytokine production from T cells, antigen-presenting cells, natural killer cells, and natural killer T cells, and modulate cytokine receptor signaling. In line with these important modulatory functions, OX40-OX40L interactions have been found to play a central role in the development of multiple inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, making them attractive candidates for intervention in the clinic. Conversely, stimulating OX40 has shown it to be a candidate for therapeutic immunization strategies for cancer and infectious disease. This review provides a broad overview of the biology of OX40 including the intracellular signals from OX40 that impact many aspects of immune function and have promoted OX40 as one of the most prominent costimulatory molecules known to control T cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
OX40 and OX40L Interaction in Cancer.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(28):5659-5673. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666201229123151. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33372866 Review.
-
OX40, OX40L and Autoimmunity: a Comprehensive Review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Jun;50(3):312-32. doi: 10.1007/s12016-015-8498-3. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26215166 Review.
-
OX40 ligand-transduced tumor cell vaccine synergizes with GM-CSF and requires CD40-Apc signaling to boost the host T cell antitumor response.J Immunol. 2003 Jan 1;170(1):99-106. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.99. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12496388
-
Intratumor OX40 stimulation inhibits IRF1 expression and IL-10 production by Treg cells while enhancing CD40L expression by effector memory T cells.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Dec;41(12):3615-26. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141700. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22229156
-
Targeting OX40 and OX40L for the treatment of autoimmunity and cancer.Crit Rev Immunol. 2007;27(5):415-36. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v27.i5.20. Crit Rev Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18197805 Review.
Cited by
-
Making the effect visible - OX40 targeting nanobodies for in vivo imaging of activated T cells.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 15;15:1480091. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1480091. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39474429 Free PMC article.
-
Activation-Induced Marker Assay to Identify and Isolate HCV-Specific T Cells for Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis.Viruses. 2024 Oct 17;16(10):1623. doi: 10.3390/v16101623. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459954 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing the treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer: the impact, challenges and strategies of stem cell and genetically engineered cell therapies.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 10;15:1484535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1484535. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39450176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Biologic Therapies for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis.Drugs. 2024 Oct 4. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-02095-4. Online ahead of print. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39365406 Review.
-
Cancer immunotherapies: A hope for the uncurable?Front Mol Med. 2023 Feb 17;3:1140977. doi: 10.3389/fmmed.2023.1140977. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 39086690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paterson DJ, et al. Antigens of activated rat T lymphocytes including a molecule of 50,000 Mr detected only on CD4 positive T blasts. Mol Immunol. 1987;24:1281–90. - PubMed
-
- Calderhead DM, Buhlmann JE, van den Eertwegh AJ, Claassen E, Noelle RJ, Fell HP. Cloning of mouse Ox40: a T cell activation marker that may mediate T-B cell interactions. J Immunol. 1993;151:5261–71. - PubMed
-
- Gramaglia I, Weinberg AD, Lemon M, Croft M. OX40 ligand: a potent costimulatory molecule for sustaining primary CD4 T cell responses. J Immunol. 1998;161:6510–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

