The mechano-activated K+ channels TRAAK and TREK-1 control both warm and cold perception
- PMID: 19279663
- PMCID: PMC2683043
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.57
The mechano-activated K+ channels TRAAK and TREK-1 control both warm and cold perception
Abstract
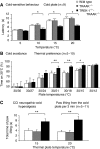
The sensation of cold or heat depends on the activation of specific nerve endings in the skin. This involves heat- and cold-sensitive excitatory transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. However, we show here that the mechano-gated and highly temperature-sensitive potassium channels of the TREK/TRAAK family, which normally work as silencers of the excitatory channels, are also implicated. They are important for the definition of temperature thresholds and temperature ranges in which excitation of nociceptor takes place and for the intensity of excitation when it occurs. They are expressed with thermo-TRP channels in sensory neurons. TRAAK and TREK-1 channels control pain produced by mechanical stimulation and both heat and cold pain perception in mice. Expression of TRAAK alone or in association with TREK-1 controls heat responses of both capsaicin-sensitive and capsaicin-insensitive sensory neurons. Together TREK-1 and TRAAK channels are important regulators of nociceptor activation by cold, particularly in the nociceptor population that is not activated by menthol.
Figures
Comment in
-
TREKing noxious thermosensation.EMBO J. 2009 May 6;28(9):1195-6. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.107. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19421163 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
TREKing noxious thermosensation.EMBO J. 2009 May 6;28(9):1195-6. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.107. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19421163 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Thermosensitivity of the two-pore domain K+ channels TREK-2 and TRAAK.J Physiol. 2005 Apr 1;564(Pt 1):103-16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.081059. Epub 2005 Jan 27. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15677687 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of K2P channels in sensory and motor neurons of the autonomic nervous system.J Mol Neurosci. 2012 Sep;48(1):86-96. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9780-y. Epub 2012 Apr 29. J Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22544515
-
Temperature sensitivity of two-pore (K2P) potassium channels.Curr Top Membr. 2014;74:113-33. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800181-3.00005-1. Curr Top Membr. 2014. PMID: 25366235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid and mechano-gated 2P domain K(+) channels.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;13(4):422-8. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00231-3. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11454447 Review.
Cited by
-
The family of K2P channels: salient structural and functional properties.J Physiol. 2015 Jun 15;593(12):2587-603. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.287268. Epub 2015 Jan 22. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25530075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of capsaicin on thermoregulation: an update with new aspects.Temperature (Austin). 2015 Jun 2;2(2):277-96. doi: 10.1080/23328940.2015.1048928. eCollection 2015 Apr-Jun. Temperature (Austin). 2015. PMID: 27227029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-throughput functional screen identifies small molecule regulators of temperature- and mechano-sensitive K2P channels.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Aug 16;8(8):1841-51. doi: 10.1021/cb400289x. Epub 2013 Jun 17. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23738709 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC3 and TRPC6 are essential for normal mechanotransduction in subsets of sensory neurons and cochlear hair cells.Open Biol. 2012 May;2(5):120068. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120068. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22724068 Free PMC article.
-
Electromechanical model for object roughness perception during finger sliding.Biophys J. 2022 Dec 6;121(23):4740-4747. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.09.014. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 36116008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahamsen B, Zhao J, Asante CO, Cendan CM, Marsh S, Martinez-Barbera JP, Nassar MA, Dickenson AH, Wood JN (2008) The cell and molecular basis of mechanical, cold, and inflammatory pain. Science 321: 702–705 - PubMed
-
- Alessandri-Haber N, Joseph E, Dina OA, Liedtke W, Levine JD (2005) TRPV4 mediates pain-related behavior induced by mild hypertonic stimuli in the presence of inflammatory mediator. Pain 118: 70–79 - PubMed
-
- Babes A, Zorzon D, Reid G (2004) Two populations of cold-sensitive neurons in rat dorsal root ganglia and their modulation by nerve growth factor. Eur J Neurosci 20: 2276–2282 - PubMed
-
- Babes A, Zorzon D, Reid G (2006) A novel type of cold-sensitive neuron in rat dorsal root ganglia with rapid adaptation to cooling stimuli. Eur J Neurosci 24: 691–698 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

