Comparative functional analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster proteomes
- PMID: 19260763
- PMCID: PMC2650730
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000048
Comparative functional analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster proteomes
Abstract
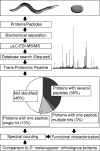
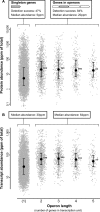
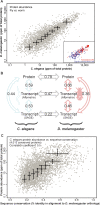
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is a popular model system in genetics, not least because a majority of human disease genes are conserved in C. elegans. To generate a comprehensive inventory of its expressed proteome, we performed extensive shotgun proteomics and identified more than half of all predicted C. elegans proteins. This allowed us to confirm and extend genome annotations, characterize the role of operons in C. elegans, and semiquantitatively infer abundance levels for thousands of proteins. Furthermore, for the first time to our knowledge, we were able to compare two animal proteomes (C. elegans and Drosophila melanogaster). We found that the abundances of orthologous proteins in metazoans correlate remarkably well, better than protein abundance versus transcript abundance within each organism or transcript abundances across organisms; this suggests that changes in transcript abundance may have been partially offset during evolution by opposing changes in protein abundance.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Drosophila melanogaster flightless-I gene involved in gastrulation and muscle degeneration encodes gelsolin-like and leucine-rich repeat domains and is conserved in Caenorhabditis elegans and humans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11386-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11386. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8248259 Free PMC article.
-
The immunoglobulin superfamily in Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans and the evolution of complexity.Development. 2003 Dec;130(25):6317-28. doi: 10.1242/dev.00848. Development. 2003. PMID: 14623821
-
Relative contributions of intrinsic structural-functional constraints and translation rate to the evolution of protein-coding genes.Genome Biol Evol. 2010 Jul 12;2:190-9. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evq010. Genome Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20624725 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomics of ionotropic acetylcholine receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster.Novartis Found Symp. 2002;245:240-57; discussion 257-60, 261-4. Novartis Found Symp. 2002. PMID: 12027012 Review.
-
An overview of the insulin signaling pathway in model organisms Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans.Peptides. 2021 Nov;145:170640. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2021.170640. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Peptides. 2021. PMID: 34450203 Review.
Cited by
-
Stabilizing selection and adaptation shape cis and trans gene expression variation in C. elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 18:2024.10.15.618466. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.15.618466. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39464158 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Dual proteomics of Drosophila melanogaster hemolymph infected with the heritable endosymbiont Spiroplasma poulsonii.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 29;16(4):e0250524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250524. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33914801 Free PMC article.
-
Directed shotgun proteomics guided by saturated RNA-seq identifies a complete expressed prokaryotic proteome.Genome Res. 2013 Nov;23(11):1916-27. doi: 10.1101/gr.151035.112. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23878158 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous extracellular matrix proteins decrease cardiac fibroblast activation in stiffening microenvironment through CAPG.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021 Oct;159:105-119. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 10. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34118218 Free PMC article.
-
PhyloQuant approach provides insights into Trypanosoma cruzi evolution using a systems-wide mass spectrometry-based quantitative protein profile.Commun Biol. 2021 Mar 11;4(1):324. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01762-6. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33707618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Brien KP, Westerlund I, Sonnhammer EL. OrthoDisease: a database of human disease orthologs. Hum Mutat. 2004;24:112–119. - PubMed
-
- C. elegans Sequencing Consortium. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. Science. 1998;282:2012–2018. - PubMed
-
- Anderson L, Seilhamer J. A comparison of selected mRNA and protein abundances in human liver. Electrophoresis. 1997;18:533–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

