Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit chondrogenesis by human mesenchymal stem cells through NF-kappaB-dependent pathways
- PMID: 19248089
- PMCID: PMC2688727
- DOI: 10.1002/art.24352
Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit chondrogenesis by human mesenchymal stem cells through NF-kappaB-dependent pathways
Abstract
Objective: The differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) into chondrocytes provides an attractive basis for the repair and regeneration of articular cartilage. Under clinical conditions, chondrogenesis will often need to occur in the presence of mediators of inflammation produced in response to injury or disease. The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of 2 important inflammatory cytokines, interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha), on the chondrogenic behavior of human MSCs.
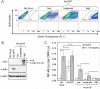
Methods: Aggregate cultures of MSCs recovered from the femoral intermedullary canal were used. Chondrogenesis was assessed by the expression of relevant transcripts by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis and examination of aggregates by histologic and immunohistochemical analyses. The possible involvement of NF-kappaB in mediating the effects of IL-1beta was examined by delivering a luciferase reporter construct and a dominant-negative inhibitor of NF-kappaB (suppressor-repressor form of IkappaB [srIkappaB]) with adenovirus vectors.
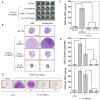
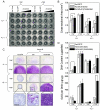
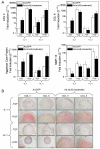
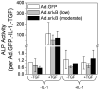
Results: Both IL-1beta and TNFalpha inhibited chondrogenesis in a dose-dependent manner. This was associated with a marked activation of NF-kappaB. Delivery of srIkappaB abrogated the activation of NF-kappaB and rescued the chondrogenic response. Although expression of type X collagen followed this pattern, other markers of hypertrophic differentiation responded differently. Matrix metalloproteinase 13 was induced by IL-1beta in a NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Alkaline phosphatase activity, in contrast, was inhibited by IL-1beta regardless of srIkappaB delivery.
Conclusion: Cell-based repair of lesions in articular cartilage will be compromised in inflamed joints. Strategies for enabling repair under these conditions include the use of specific antagonists of individual pyrogens, such as IL-1beta and TNFalpha, or the targeting of important intracellular mediators, such as NF-kappaB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin mediated suppression of nuclear factor-κB promotes chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in a high-density co-culture microenvironment.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):R127. doi: 10.1186/ar3065. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20594343 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) is required for promoting chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 8;289(32):22048-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.568790. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24962570 Free PMC article.
-
Physioxia Has a Beneficial Effect on Cartilage Matrix Production in Interleukin-1 Beta-Inhibited Mesenchymal Stem Cell Chondrogenesis.Cells. 2019 Aug 20;8(8):936. doi: 10.3390/cells8080936. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31434236 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Signaling Regulates Physiological and Pathological Chondrogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 12;20(24):6275. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246275. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31842396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-kappaB function in the human myometrium during pregnancy and parturition.Histol Histopathol. 2010 Jul;25(7):945-56. doi: 10.14670/HH-25.945. Histol Histopathol. 2010. PMID: 20503182 Review.
Cited by
-
TNFα has differential effects on the transcriptome profile of selected populations in murine cartilage.Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2024 Oct 10;6(4):100528. doi: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2024.100528. eCollection 2024 Dec. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2024. PMID: 39494399 Free PMC article.
-
TNFα-Related Chondrocyte Inflammation Models: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 8;25(19):10805. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910805. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Exosomes of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Suppress Inflammation in Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 6;25(16):8560. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168560. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201248 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsed electromagnetic fields potentiate bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Transl Med. 2024 Aug 6;22(1):741. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05470-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39107784 Free PMC article.
-
A synthetic, closed-looped gene circuit for the autonomous regulation of RUNX2 activity during chondrogenesis.FASEB J. 2024 Feb 29;38(4):e23484. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300348RR. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38407380
References
-
- Simon TM, Jackson DW. Articular cartilage: injury pathways and treatment options. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2006;14(3):146–54. - PubMed
-
- Djouad F, Mrugala D, Noel D, Jorgensen C. Engineered mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage repair. Regen Med. 2006;1(4):529–37. - PubMed
-
- Pountos I, Corscadden D, Emery P, Giannoudis PV. Mesenchymal stem cell tissue engineering: techniques for isolation, expansion and application. Injury. 2007;38(Suppl 4):S23–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources