The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy
- PMID: 19247306
- PMCID: PMC3684054
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd2792
The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy
Abstract
The family of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) regulates a plethora of developmental processes, including brain patterning, branching morphogenesis and limb development. Several mitogenic, cytoprotective and angiogenic therapeutic applications of FGFs are already being explored, and the recent discovery of the crucial roles of the endocrine-acting FGF19 subfamily in bile acid, glucose and phosphate homeostasis has sparked renewed interest in the pharmacological potential of this family. This Review discusses traditional applications of recombinant FGFs and small-molecule FGF receptor kinase inhibitors in the treatment of cancer and cardiovascular disease and their emerging potential in the treatment of metabolic syndrome and hypophosphataemic diseases.
Figures
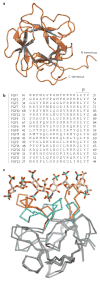
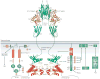
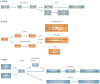
Similar articles
-
FGF Family: From Drug Development to Clinical Application.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 26;19(7):1875. doi: 10.3390/ijms19071875. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29949887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Saga of Endocrine FGFs.Cells. 2021 Sep 14;10(9):2418. doi: 10.3390/cells10092418. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of the endocrine fibroblast growth factors FGF19, FGF21 and FGF23.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Jan;15(1):51-69. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2015.9. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 26567701 Review.
-
Therapeutic utilities of fibroblast growth factor 19.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011 Nov;15(11):1307-16. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.624514. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011. PMID: 21961833 Review.
-
Endocrine fibroblast growth factors as regulators of metabolic homeostasis.Biofactors. 2009 Jan-Feb;35(1):52-60. doi: 10.1002/biof.12. Biofactors. 2009. PMID: 19319846 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced expression of FGF19 predicts poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Mar;13(3):1769-1784. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-126. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 33841967 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a Potent Degrader for Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1/2.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Jul 12;60(29):15905-15911. doi: 10.1002/anie.202101328. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33915015 Free PMC article.
-
The coexpression and prognostic significance of c-MET, fibroblast growth factor receptor 2, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 in resected gastric cancer: a retrospective study.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Sep 27;9:5919-5929. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S111778. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27729801 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-34a and Impaired FGF19/21 Signaling in Obesity.Vitam Horm. 2016;101:175-96. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2016.02.002. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Vitam Horm. 2016. PMID: 27125742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGFs: Neurodevelopment's Jack-of-all-Trades - How Do They Do it?Front Neurosci. 2011 Dec 5;5:133. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2011.00133. eCollection 2011. Front Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22164131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Itoh N, Ornitz DM. Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet. 2004;20:563–569. - PubMed
-
- Olsen SK, et al. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) homologous factors share structural but not functional homology with FGFs. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:34226–34236. - PubMed
-
- Fu L, et al. Fibroblast growth factor19 increases metabolic rate and reverses dietary and leptin-deficient diabetes. Endocrinology. 2004;145:2594–2603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

