Noncanonical NF-kappaB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK
- PMID: 18997794
- PMCID: PMC2676931
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1676
Noncanonical NF-kappaB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK
Abstract
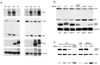
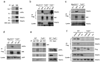
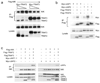
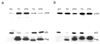
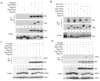
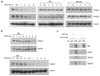
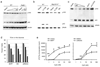
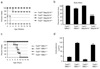
Recent studies suggest that nuclear factor kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) is suppressed through constitutive proteasome-mediated degradation regulated by TRAF2, TRAF3 and cIAP1 or cIAP2. Here we demonstrated that the degradation of NIK occurs upon assembly of a regulatory complex through TRAF3 recruitment of NIK and TRAF2 recruitment of cIAP1 and cIAP2. In contrast to TRAF2 and TRAF3, cIAP1 and cIAP2 seem to play redundant roles in the degradation of NIK, as inhibition of both cIAPs was required for noncanonical NF-kappaB activation and increased survival and proliferation of primary B lymphocytes. Furthermore, the lethality of TRAF3 deficiency in mice could be rescued by a single NIK gene, highlighting the importance of tightly regulated NIK.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-kappaB signaling.Nat Immunol. 2008 Dec;9(12):1364-70. doi: 10.1038/ni.1678. Epub 2008 Nov 9. Nat Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18997792 Free PMC article.
-
TACI induces cIAP1-mediated ubiquitination of NIK by TRAF2 and TANK to limit non-canonical NF-kappaB signaling.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010 Apr;30(2):121-32. doi: 10.3109/10799891003634509. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010. PMID: 20184394
-
Deletion of cIAP1 and cIAP2 in murine B lymphocytes constitutively activates cell survival pathways and inactivates the germinal center response.Blood. 2011 Apr 14;117(15):4041-51. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-10-312793. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21300983
-
Targeting signaling factors for degradation, an emerging mechanism for TRAF functions.Immunol Rev. 2015 Jul;266(1):56-71. doi: 10.1111/imr.12311. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26085207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-canonical NF-κB signaling activation and regulation: principles and perspectives.Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):44-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01059.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22017430 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of cIAP1 attenuates soleus muscle pathology and improves diaphragm function in mdx mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Mar 1;22(5):867-78. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds493. Epub 2012 Nov 25. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23184147 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of TRAF3 in T cells: many surprises.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(8):1156-63. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1021524. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25723057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitylation in immune disorders and cancer: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic implications.EMBO Mol Med. 2012 Jul;4(7):545-56. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100707. Epub 2012 Jun 25. EMBO Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22730341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High doses of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides stimulate a tolerogenic TLR9-TRIF pathway.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1852. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2874. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23673637
-
Osteoclast fusion and regulation by RANKL-dependent and independent factors.World J Orthop. 2012 Dec 18;3(12):212-22. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v3.i12.212. World J Orthop. 2012. PMID: 23362465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Iotsova V, et al. Osteopetrosis in mice lacking NF-κB1 and NF-κB2. Nat Med. 1997;3:1285–1289. - PubMed
-
- Kopp EB, Ghosh S. NF-κB and rel proteins in innate immunity. Adv Immunol. 1995;58:1–27. - PubMed
-
- Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF-κB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:280–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

