The role of Ephs, Ephrins, and growth factors in Kaposi sarcoma and implications of EphrinB2 blockade
- PMID: 18836096
- PMCID: PMC2614637
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-140020
The role of Ephs, Ephrins, and growth factors in Kaposi sarcoma and implications of EphrinB2 blockade
Abstract
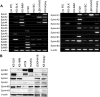
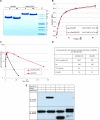
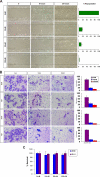
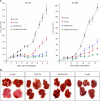
Kaposi sarcoma (KS) is associated with human herpesvirus (HHV)-8 and is dependent on the induction of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs). VEGF regulates genes that provide arterial or venous identity to endothelial cells, such as the induction of EphrinB2, which phenotypically defines arterial endothelial cells and pericytes, and represses EphB4, which defines venous endothelial cells. We conducted a comprehensive analysis of the Eph receptor tyrosine kinases to determine which members are expressed and therefore contribute to KS pathogenesis. We demonstrated limited Eph/Ephrin expression; notably, the only ligand highly expressed is EphrinB2. We next studied the biologic effects of blocking EphrinB2 using the extracellular domain of EphB4 fused with human serum albumin (sEphB4-HSA). sEphB4-HSA inhibited migration and invasion of the KS cells in vitro in response to various growth factors. Finally, we determined the biologic effects of combining sEphB4-HSA and an antibody to VEGF. sEphB4-HSA was more active than the VEGF antibody, and combination of the 2 had at least additive activity. sEphB4-HSA reduced blood vessel density, pericyte recruitment, vessel perfusion, and increased hypoxia, with an associated increase in VEGF and DLL4 expression. The combination of sEphB4-HSA and VEGF antibody is a rational treatment combination for further investigation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of Dll4/Notch and Ephrin-B2/EphB4 targeted therapy is highly effective in disrupting tumor angiogenesis.BMC Cancer. 2010 Nov 23;10:641. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-641. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21092311 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between EphB4 on tumor cells and vascular ephrin-B2 regulates tumor growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 13;101(15):5583-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401381101. Epub 2004 Apr 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15067119 Free PMC article.
-
EphB ligand, ephrinB2, suppresses the VEGF- and angiopoietin 1-induced Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in venous endothelial cells.FASEB J. 2002 Jul;16(9):1126-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0805fje. Epub 2002 May 21. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 12039842
-
The critical role of the interplays of EphrinB2/EphB4 and VEGF in the induction of angiogenesis.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jun;47(6):4681-4690. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05470-y. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32488576 Review.
-
Regulation of signaling interactions and receptor endocytosis in growing blood vessels.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(4):366-77. doi: 10.4161/19336918.2014.970010. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 25482636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic targeting of EPH receptors and their ligands.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014 Jan;13(1):39-62. doi: 10.1038/nrd4175. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 24378802 Review.
-
EphrinB2 expression in prostate adenocarcinoma: Implications for targeted therapy.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Jun;216(6):152967. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.152967. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32362422 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 inhibitors are efficacious against Kaposi Sarcoma by enhancing the degradation of the essential viral gene LANA, of the viral co-receptor EphA2 as well as other client proteins.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(11):e1003048. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003048. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23209418 Free PMC article.
-
High serum Ephrin-B2 levels predict poor prognosis for patients with gastric cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Oct;16(4):4455-4461. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9202. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30214580 Free PMC article.
-
The differential expression of EphB2 and EphB4 receptor kinases in normal bladder and in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 22;9(8):e105326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105326. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25148033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ. Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4. Cell. 1998;93:741–753. - PubMed
-
- Sivakumar R, Sharma-Walia N, Raghu H, et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces sustained levels of vascular endothelial growth factors A and C early during in vitro infection of human microvascular dermal endothelial cells: biological implications. J Virol. 2008;82:1759–1776. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gerety SS, Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ. Symmetrical mutant phenotypes of the receptor EphB4 and its specific transmembrane ligand ephrin-B2 in cardiovascular development. Mol Cell. 1999;4:403–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

