The canonical Wnt signaling pathway plays an important role in lymphopoiesis and hematopoiesis
- PMID: 18581335
- PMCID: PMC2556850
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200738118
The canonical Wnt signaling pathway plays an important role in lymphopoiesis and hematopoiesis
Abstract
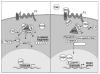
The evolutionarily conserved canonical Wnt-beta-catenin-T cell factor (TCF)/lymphocyte enhancer binding factor (LEF) signaling pathway regulates key checkpoints in the development of various tissues. Therefore, it is not surprising that a large body of gain-of-function and loss-of-function studies implicate Wnt-beta-catenin signaling in lymphopoiesis and hematopoiesis. In contrast, recent papers have reported that Mx-Cre-mediated conditional deletion of beta-catenin and/or its homolog gamma-catenin (plakoglobin) did not impair hematopoiesis or lymphopoiesis. However, these studies also report that TCF reporter activity remains active in beta-catenin- and gamma-catenin-deficient hematopoietic stem cells and all cells derived from these precursors, indicating that the canonical Wnt signaling pathway was not abrogated. Therefore, these studies in fact show that the canonical Wnt signaling pathway is important in hematopoiesis and lymphopoiesis, even though the molecular basis for the induction of the reporter activity is currently unknown. In this perspective, we provide a broad background to the field with a discussion of the available data and create a framework within which the available and future studies may be evaluated.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Canonical Wnt signalling plays essential roles.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Dec;39(12):3582-3; author reply 3583-4. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838982. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19941311 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Canonical Wnt signalling plays essential roles.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Dec;39(12):3582-3; author reply 3583-4. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838982. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19941311 No abstract available.
-
Simultaneous loss of beta- and gamma-catenin does not perturb hematopoiesis or lymphopoiesis.Blood. 2008 Jan 1;111(1):160-4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-07-099754. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Blood. 2008. PMID: 17855627
-
Wnt expression and canonical Wnt signaling in human bone marrow B lymphopoiesis.BMC Immunol. 2006 Jun 29;7:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-7-13. BMC Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16808837 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling in lymphopoiesis.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;290:225-52. doi: 10.1007/3-540-26363-2_10. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16480045 Review.
-
Wnt signaling in hematopoiesis: crucial factors for self-renewal, proliferation, and cell fate decisions.J Cell Biochem. 2010 Apr 1;109(5):844-9. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22467. J Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20069555 Review.
Cited by
-
Th17 cells are long lived and retain a stem cell-like molecular signature.Immunity. 2011 Dec 23;35(6):972-85. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.09.019. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Immunity. 2011. PMID: 22177921 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical Wnt signaling in megakaryocytes regulates proplatelet formation.Blood. 2013 Jan 3;121(1):188-96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-416875. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23160460 Free PMC article.
-
The E protein-TCF1 axis controls γδ T cell development and effector fate.Cell Rep. 2021 Feb 2;34(5):108716. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108716. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 33535043 Free PMC article.
-
T cell factor-1 controls the lifetime of CD4+ CD8+ thymocytes in vivo and distal T cell receptor α-chain rearrangement required for NKT cell development.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 23;9(12):e115803. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115803. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25536344 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional silencing of the Wnt-antagonist DKK1 by promoter methylation is associated with enhanced Wnt signaling in advanced multiple myeloma.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030359. Epub 2012 Feb 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, Duncan AW, Weissman IL, Reya T, Yates JR, 3rd, Nusse R. Wnt proteins are lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature. 2003;423:448–452. - PubMed
-
- Staal FJ, Clevers HC. Wnt signalling and haematopoiesis: A Wnt-Wnt situation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:21–30. - PubMed
-
- Brembeck FH, Rosario M, Birchmeier W. Balancing cell adhesion and Wnt signaling, the key role of beta-catenin. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16:51–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

