Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A preferentially signals through the Src family kinase Lyn
- PMID: 18579586
- PMCID: PMC2519656
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00843-08
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A preferentially signals through the Src family kinase Lyn
Abstract
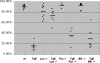
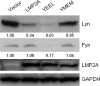
Latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) is a viral protein expressed during Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latency in EBV-infected B cells both in cell culture and in vivo. LMP2A has important roles in modulating B-cell receptor signal transduction and provides survival and developmental signals to B cells in vivo. Although Lyn has been shown to be important in mediating LMP2A signaling, it is still unclear if Lyn is used preferentially or if LMP2A associates promiscuously with other Src family kinase (SFK) members. To investigate the role of various SFKs in LMP2A signaling, we crossed LMP2A transgenic mice (TgE) with Lyn(-/-), Fyn(-/-), or Blk(-/-) mice. TgE Lyn(-/-) mice had a larger immunoglobulin M (IgM)-positive B-cell population than TgE mice, suggesting that the absence of Lyn prevents LMP2A from delivering survival and developmental signals to the B cells. Both TgE Fyn(-/-) and TgE Blk(-/-) mice have an IgM-negative population of splenic B cells, similar to the TgE mice. LMP2A was also transiently transfected into the human EBV-negative B-cell line BJAB to determine which SFK members associate with LMP2A. Lyn was detected in LMP2A immunoprecipitates, whereas Fyn was not. Both Lyn and Fyn were able to bind to an LMP2A mutant which contained a sequence shown previously to bind tightly to the SH2 domain of multiple SFK members. From these results, we conclude that LMP2A preferentially associates with and signals through Lyn compared to its association with other SFKs. This preferential association is due in part to the SH2 domain of Lyn associating with LMP2A.
Figures

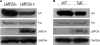

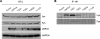
Similar articles
-
Latent membrane protein 2A of Epstein-Barr virus binds WW domain E3 protein-ubiquitin ligases that ubiquitinate B-cell tyrosine kinases.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Nov;20(22):8526-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.22.8526-8535.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11046148 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine 112 of latent membrane protein 2A is essential for protein tyrosine kinase loading and regulation of Epstein-Barr virus latency.J Virol. 1998 Oct;72(10):7796-806. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.10.7796-7806.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9733815 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A-induced B-cell survival in two unique classes of EmuLMP2A transgenic mice.J Virol. 2000 Feb;74(3):1101-13. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.3.1101-1113.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10627520 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A on B cell function.Int Rev Immunol. 2001;20(6):805-35. doi: 10.3109/08830180109045591. Int Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11913951 Review.
-
Latent Membrane Protein 2 (LMP2).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:151-80. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428374 Review.
Cited by
-
EBV latent membrane protein 2A orchestrates p27kip1 degradation via Cks1 to accelerate MYC-driven lymphoma in mice.Blood. 2017 Dec 7;130(23):2516-2526. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-07-796821. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Blood. 2017. PMID: 29074502 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent genes.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Jan 23;47(1):e131. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.84. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25613728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening and functional analysis of differentially expressed genes in EBV-transformed lymphoblasts.Virol J. 2012 Mar 30;9:77. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-77. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22458412 Free PMC article.
-
Cancers associated with human gammaherpesviruses.FEBS J. 2022 Dec;289(24):7631-7669. doi: 10.1111/febs.16206. Epub 2021 Oct 2. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34536980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor-mediated invasion of Streptococcus pneumoniae into host cells requires a coordinate signaling of SRC family of protein-tyrosine kinases, ERK, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 12;285(46):35615-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.172999. Epub 2010 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20829350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babcock, G. J., L. L. Decker, M. Volk, and D. A. Thorley-Lawson. 1998. EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity 9395-404. - PubMed
-
- Babcock, G. J., D. Hochberg, and A. D. Thorley-Lawson. 2000. The expression pattern of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes in vivo is dependent upon the differentiation stage of the infected B cell. Immunity 13497-506. - PubMed
-
- Bobbitt, K. R., and L. B. Justement. 2000. Regulation of MHC class II signal transduction by the B cell coreceptors CD19 and CD22. J. Immunol. 1655588-5596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

