RNA-seq: an assessment of technical reproducibility and comparison with gene expression arrays
- PMID: 18550803
- PMCID: PMC2527709
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.079558.108
RNA-seq: an assessment of technical reproducibility and comparison with gene expression arrays
Abstract
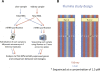
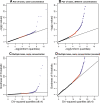
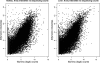
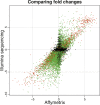
Ultra-high-throughput sequencing is emerging as an attractive alternative to microarrays for genotyping, analysis of methylation patterns, and identification of transcription factor binding sites. Here, we describe an application of the Illumina sequencing (formerly Solexa sequencing) platform to study mRNA expression levels. Our goals were to estimate technical variance associated with Illumina sequencing in this context and to compare its ability to identify differentially expressed genes with existing array technologies. To do so, we estimated gene expression differences between liver and kidney RNA samples using multiple sequencing replicates, and compared the sequencing data to results obtained from Affymetrix arrays using the same RNA samples. We find that the Illumina sequencing data are highly replicable, with relatively little technical variation, and thus, for many purposes, it may suffice to sequence each mRNA sample only once (i.e., using one lane). The information in a single lane of Illumina sequencing data appears comparable to that in a single array in enabling identification of differentially expressed genes, while allowing for additional analyses such as detection of low-expressed genes, alternative splice variants, and novel transcripts. Based on our observations, we propose an empirical protocol and a statistical framework for the analysis of gene expression using ultra-high-throughput sequencing technology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic comparison and evaluation of high density exon arrays and RNA-seq technology used to unravel the peripheral blood transcriptome of sickle cell disease.BMC Med Genomics. 2012 Jun 29;5:28. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-5-28. BMC Med Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22747986 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating gene expression in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mouse striatum using RNA-Seq and microarrays.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 24;6(3):e17820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017820. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21455293 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating accuracy of RNA-Seq and microarrays with proteomics.BMC Genomics. 2009 Apr 16;10:161. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-161. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19371429 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical detection of differentially expressed genes based on RNA-seq: from biological to phylogenetic replicates.Brief Bioinform. 2016 Mar;17(2):243-8. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv035. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Brief Bioinform. 2016. PMID: 26108230 Review.
-
Microarrays, deep sequencing and the true measure of the transcriptome.BMC Biol. 2011 May 31;9:34. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-9-34. BMC Biol. 2011. PMID: 21627854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A preliminary study of gene expression changes in Koalas Infected with Koala Retrovirus (KoRV) and identification of potential biomarkers for KoRV pathogenesis.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Oct 30;20(1):496. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04357-5. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39478576 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Analysis of RNA-Seq Data Identifies Key Gene Signatures and Pathways in Mpox Virus-Induced Gastrointestinal Complications Using Colon Organoid Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 17;25(20):11142. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011142. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456924 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Gossypol on Gene Expression in Swine Granulosa Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;16(10):436. doi: 10.3390/toxins16100436. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39453212 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell profiling of cellular changes in the somatic peripheral nerves following nerve injury.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 2;15:1448253. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1448253. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39415832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BayesAge 2.0: A Maximum Likelihood Algorithm to Predict Transcriptomic Age.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 19:2024.09.16.613354. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.16.613354. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345375 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Allison D., Cui X., Page G., Sabripour M., Cui X., Page G., Sabripour M., Page G., Sabripour M., Sabripour M. Microarray data analysis: From disarray to consolidation and consensus. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:55–65. - PubMed
-
- Bennett S., Barnes C., Cox A., Davies L., Brown C., Barnes C., Cox A., Davies L., Brown C., Cox A., Davies L., Brown C., Davies L., Brown C., Brown C. Toward the 1,000 dollars human genome. Pharmacogenomics. 2005;6:373–382. - PubMed
-
- Cokus S., Feng S., Zhang X., Chen Z., Merriman B., Haudenschild C., Pradhan S., Nelson S., Pellegrini M., Jacobsen S., Feng S., Zhang X., Chen Z., Merriman B., Haudenschild C., Pradhan S., Nelson S., Pellegrini M., Jacobsen S., Zhang X., Chen Z., Merriman B., Haudenschild C., Pradhan S., Nelson S., Pellegrini M., Jacobsen S., Chen Z., Merriman B., Haudenschild C., Pradhan S., Nelson S., Pellegrini M., Jacobsen S., Merriman B., Haudenschild C., Pradhan S., Nelson S., Pellegrini M., Jacobsen S., Haudenschild C., Pradhan S., Nelson S., Pellegrini M., Jacobsen S., Pradhan S., Nelson S., Pellegrini M., Jacobsen S., Nelson S., Pellegrini M., Jacobsen S., Pellegrini M., Jacobsen S., Jacobsen S. Shotgun bisulphite sequencing of the Arabidopsis genome reveals DNA methylation patterning. Nature. 2008;452:215–219. - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Jonge H., Fehrmann R., de Bont E., Hofstra R., Gerbens F., Kamps W., de Vries E., van der Zee A., te Meerman G., ter Elst A., Fehrmann R., de Bont E., Hofstra R., Gerbens F., Kamps W., de Vries E., van der Zee A., te Meerman G., ter Elst A., de Bont E., Hofstra R., Gerbens F., Kamps W., de Vries E., van der Zee A., te Meerman G., ter Elst A., Hofstra R., Gerbens F., Kamps W., de Vries E., van der Zee A., te Meerman G., ter Elst A., Gerbens F., Kamps W., de Vries E., van der Zee A., te Meerman G., ter Elst A., Kamps W., de Vries E., van der Zee A., te Meerman G., ter Elst A., de Vries E., van der Zee A., te Meerman G., ter Elst A., van der Zee A., te Meerman G., ter Elst A., te Meerman G., ter Elst A., ter Elst A. Evidence based selection of housekeeping genes. PLoS One. 2007;2:e898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000898. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
