MeCP2, a key contributor to neurological disease, activates and represses transcription
- PMID: 18511691
- PMCID: PMC2443785
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1153252
MeCP2, a key contributor to neurological disease, activates and represses transcription
Abstract
Mutations in the gene encoding the transcriptional repressor methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) cause the neurodevelopmental disorder Rett syndrome. Loss of function as well as increased dosage of the MECP2 gene cause a host of neuropsychiatric disorders. To explore the molecular mechanism(s) underlying these disorders, we examined gene expression patterns in the hypothalamus of mice that either lack or overexpress MeCP2. In both models, MeCP2 dysfunction induced changes in the expression levels of thousands of genes, but unexpectedly the majority of genes (approximately 85%) appeared to be activated by MeCP2. We selected six genes and confirmed that MeCP2 binds to their promoters. Furthermore, we showed that MeCP2 associates with the transcriptional activator CREB1 at the promoter of an activated target but not a repressed target. These studies suggest that MeCP2 regulates the expression of a wide range of genes in the hypothalamus and that it can function as both an activator and a repressor of transcription.
Figures
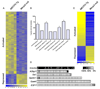
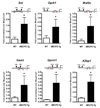
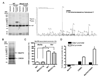
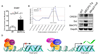
Comment in
-
Medicine. Activating a repressor.Science. 2008 May 30;320(5880):1172-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1159146. Science. 2008. PMID: 18511680 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cerebellar gene expression profiles of mouse models for Rett syndrome reveal novel MeCP2 targets.BMC Med Genet. 2007 Jun 20;8:36. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-36. BMC Med Genet. 2007. PMID: 17584923 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of MeCP2 disorders share gene expression changes in the cerebellum and hypothalamus.Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Jul 1;18(13):2431-42. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp181. Epub 2009 Apr 15. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19369296 Free PMC article.
-
MeCP2 deficiency in the brain decreases BDNF levels by REST/CoREST-mediated repression and increases TRKB production.Epigenetics. 2007 Oct-Dec;2(4):214-22. doi: 10.4161/epi.2.4.5212. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Epigenetics. 2007. PMID: 18075316
-
[Research progress of Rett syndrome causing gene MECP2--the structure, function and modulation of MECP2].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009 Dec 18;41(6):712-5. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009. PMID: 20019788 Review. Chinese.
-
MeCP2 in Rett syndrome: transcriptional repressor or chromatin architectural protein?Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007 Apr;17(2):121-5. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2007.02.003. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007. PMID: 17317146 Review.
Cited by
-
Rett syndrome mutation MeCP2 T158A disrupts DNA binding, protein stability and ERP responses.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Nov 27;15(2):274-83. doi: 10.1038/nn.2997. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22119903 Free PMC article.
-
Modifiers and Readers of DNA Modifications and Their Impact on Genome Structure, Expression, and Stability in Disease.Front Genet. 2016 Jun 21;7:115. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00115. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27446199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic and transcriptional changes associated with MeCP2 dysfunction reveal nodes for therapeutic intervention in Rett syndrome.Neurochem Int. 2021 Sep;148:105076. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105076. Epub 2021 May 26. Neurochem Int. 2021. PMID: 34048843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term home cage activity scans reveal lowered exploratory behaviour in symptomatic female Rett mice.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Aug 1;250:148-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.04.041. Epub 2013 May 1. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23643691 Free PMC article.
-
Looking beyond the DNA sequence: the relevance of DNA methylation processes for the stress-diathesis model of depression.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Feb 25;368(1615):20120251. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2012.0251. Print 2013. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23440465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

