KIR locus polymorphisms: genotyping and disease association analysis
- PMID: 18370147
- PMCID: PMC10763752
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-59745-570-1_3
KIR locus polymorphisms: genotyping and disease association analysis
Abstract
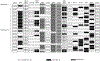
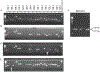
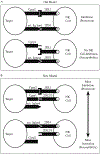
The genes encoding the killer immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) are situated within a segment of DNA that has undergone expansion and contraction over time due in large part to unequal crossing over. Consequently, individuals exhibit considerable haplotypic variation in terms of gene content. The highly polymorphic human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I loci encode ligands for the KIR; thus, it is not surprising that KIR genes also show significant allelic polymorphism. As a result of the receptor-ligand relationship between KIR and HLA, functionally relevant KIR-HLA combinations need to be considered in the analysis of these genes as they relate to disease outcomes. This chapter will describe a genotyping method for identifying the presence/absence of the KIR genes and general approaches to data analysis in disease association studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KIR genotyping by multiplex PCR-SSP.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;612:365-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-362-6_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20033654 Free PMC article.
-
KIR haplotypes defined by segregation analysis in 59 Centre d'Etude Polymorphisme Humain (CEPH) families.Immunogenetics. 2008 Dec;60(12):767-74. doi: 10.1007/s00251-008-0334-y. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Immunogenetics. 2008. PMID: 18972110 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Killer Immunoglobulin-like Receptor (KIR) and HLA Genotypes to Predict the Occurrence of Acute Allograft Rejection after Kidney Transplantation.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017 Jun;16(3):245-255. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28732438
-
KIR and KIR ligand polymorphism: a new area for clinical applications?Tissue Antigens. 2013 Dec;82(6):363-73. doi: 10.1111/tan.12262. Tissue Antigens. 2013. PMID: 24498992 Review.
-
Autoimmune rheumatic diseases and their association with killer immunoglobulin-like receptor genes.Rev Bras Reumatol. 2011 Jul-Aug;51(4):351-6, 362-4. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2011. PMID: 21779711 Review. English, Portuguese.
Cited by
-
Improving selection of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer to benefit from cetuximab based on KIR genotypes.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Apr;9(4):e001705. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001705. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33833048 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of HLA Allele-KIR Pairs on HIV Clinical Outcome in South Africa.J Infect Dis. 2019 Apr 16;219(9):1456-1463. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy692. J Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30520960 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells are recruited during pulmonary tuberculosis and their ex vivo responses to mycobacteria vary between healthy human donors in association with KIR haplotype.Cell Microbiol. 2012 Nov;14(11):1734-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01834.x. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22788220 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of KIR Genes and Their HLA Ligands in Different Viral Infectious Diseases: Frequency Study in Sicilian Population.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 7;23(24):15466. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415466. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555106 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of several activating and inhibitory receptors on CD3-CD16+ NK cells and their correlation with NK cell function in healthy individuals.J Membr Biol. 2009 Aug;230(3):113-23. doi: 10.1007/s00232-009-9191-3. Epub 2009 Aug 27. J Membr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19711124
References
-
- Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, and Caligiuri MA (2001) The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol 22, 633–40. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen KB, Salazar-Mather TP, Dalod MY, Van Deusen JB, Wei XQ, Liew FY, Caligiuri MA, Durbin JE, and Biron CA (2002) Coordinated and distinct roles for IFN-alpha beta, IL-12, and IL-15 regulation of NK cell responses to viral infection. J Immunol 169, 4279–87. - PubMed
-
- Karre K, Ljunggren HG, Piontek G, and Kiessling R (1986) Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature 319, 675–8. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu Y, and DeMars R (1989) Demonstration by class I gene transfer that reduced susceptibility of human cells to natural killer cell-mediated lysis is inversely correlated with HLA class I antigen expression. Eur J Immunol 19, 447–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

