Death by a thousand cuts: granzyme pathways of programmed cell death
- PMID: 18304003
- PMCID: PMC2790083
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090404
Death by a thousand cuts: granzyme pathways of programmed cell death
Abstract
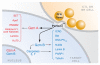
The granzymes are cell death-inducing enzymes, stored in the cytotoxic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, that are released during granule exocytosis when a specific virus-infected or transformed target cell is marked for elimination. Recent work suggests that this homologous family of serine esterases can activate at least three distinct pathways of cell death. This redundancy likely evolved to provide protection against pathogens and tumors with diverse strategies for evading cell death. This review discusses what is known about granzyme-mediated pathways of cell death as well as recent studies that implicate granzymes in immune regulation and extracellular proteolytic functions in inflammation.
Figures


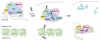
Similar articles
-
Orphan granzymes find a home.Immunol Rev. 2010 May;235(1):117-27. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00889.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20536559 Review.
-
Granzymes and cell death.Methods Enzymol. 2008;442:213-30. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)01411-0. Methods Enzymol. 2008. PMID: 18662572
-
Functional dissection of the granzyme family: cell death and inflammation.Immunol Rev. 2010 May;235(1):73-92. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00907.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20536556 Review.
-
Biology of granzyme M: a serine protease with unique features.Crit Rev Immunol. 2009;29(4):307-15. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v29.i4.20. Crit Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19673685 Review.
-
The ABCs of granule-mediated cytotoxicity: new weapons in the arsenal.Nat Rev Immunol. 2003 May;3(5):361-70. doi: 10.1038/nri1083. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12766758 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel tumour suppressor roles for GZMA and RASGRP1 in Theileria annulata-transformed macrophages and human B lymphoma cells.Cell Microbiol. 2020 Dec;22(12):e13255. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13255. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Cell Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32830401 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Blood CD8+ T-Lymphocyte Immune Response in Benign and Subpopulations of Breast Cancer Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 11;25(12):6423. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126423. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928129 Free PMC article.
-
Granzyme A inhibition reduces inflammation and increases survival during abdominal sepsis.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 30;11(8):3781-3795. doi: 10.7150/thno.49288. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33664861 Free PMC article.
-
Intraepithelial lymphocytes are associated with epithelial injury in feline intestinal T-cell lymphoma.J Vet Med Sci. 2024 Jan 26;86(1):101-110. doi: 10.1292/jvms.23-0339. Epub 2023 Dec 8. J Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38072403 Free PMC article.
-
CD8 T cell response and its released cytokine IFN-γ are necessary for lung alveolar epithelial repair during bacterial pneumonia.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 26;14:1268078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1268078. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37954603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Russell JH, Ley TJ. Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:323–70. - PubMed
-
- Gondek DC, Lu LF, Quezada SA, Sakaguchi S, Noelle RJ. Cutting edge: contact-mediated suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells involves a granzyme B-dependent, perforin-independent mechanism. J. Immunol. 2005;174:1783–86. - PubMed
-
- Grossman WJ, Verbsky JW, Tollefsen BL, Kemper C, Atkinson JP, Ley TJ. Differential expression of granzymes A and B in human cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets and T regulatory cells. Blood. 2004;104:2840–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

