Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encodes an ortholog of miR-155
- PMID: 17881434
- PMCID: PMC2169101
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01804-07
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encodes an ortholog of miR-155
Abstract
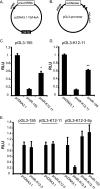
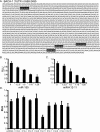
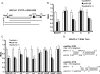
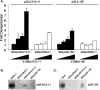
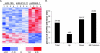
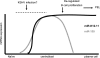
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that posttranscriptionally regulate gene expression by binding to 3'-untranslated regions (3'UTRs) of target mRNAs. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), a virus linked to malignancies including primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), encodes 12 miRNA genes, but only a few regulatory targets are known. We found that KSHV-miR-K12-11 shares 100% seed sequence homology with hsa-miR-155, an miRNA frequently found to be up-regulated in lymphomas and critically important for B-cell development. Based on this seed sequence homology, we hypothesized that both miRNAs regulate a common set of target genes and, as a result, could have similar biological activities. Examination of five PEL lines showed that PELs do not express miR-155 but do express high levels of miR-K12-11. Bioinformatic tools predicted the transcriptional repressor BACH-1 to be targeted by both miRNAs, and ectopic expression of either miR-155 or miR-K12-11 inhibited a BACH-1 3'UTR-containing reporter. Furthermore, BACH-1 protein levels are low in cells expressing either miRNA. Gene expression profiling of miRNA-expressing stable cell lines revealed 66 genes that were commonly down-regulated. For select genes, miRNA targeting was confirmed by reporter assays. Thus, based on our in silico predictions, reporter assays, and expression profiling data, miR-K12-11 and miR-155 regulate a common set of cellular targets. Given the role of miR-155 during B-cell maturation, we speculate that miR-K12-11 may contribute to the distinct developmental phenotype of PEL cells, which are blocked in a late stage of B-cell development. Together, these findings indicate that KSHV miR-K12-11 is an ortholog of miR-155.
Figures

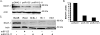
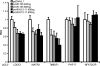
Similar articles
-
A viral microRNA functions as an orthologue of cellular miR-155.Nature. 2007 Dec 13;450(7172):1096-9. doi: 10.1038/nature05992. Nature. 2007. PMID: 18075594 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus microRNAs repress breakpoint cluster region protein expression, enhance Rac1 activity, and increase in vitro angiogenesis.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4249-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03687-14. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25631082 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Cross-Linking, Ligation, and Sequencing of Hybrids (qCLASH) Identifies Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus MicroRNA Targets in Endothelial Cells.J Virol. 2018 Mar 28;92(8):e02138-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02138-17. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29386283 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
KSHV miRNAs decrease expression of lytic genes in latently infected PEL and endothelial cells by targeting host transcription factors.Viruses. 2014 Oct 23;6(10):4005-23. doi: 10.3390/v6104005. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25341664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virus-encoded microRNAs: an overview and a look to the future.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Dec;8(12):e1003018. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003018. Epub 2012 Dec 20. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23308061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and viral microRNAs in sepsis: mechanisms of action and clinical applications.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Dec;23(12):1906-1918. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.94. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 27740627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Divergent target recognition by coexpressed 5'-isomiRs of miR-142-3p and selective viral mimicry.RNA. 2015 Sep;21(9):1606-20. doi: 10.1261/rna.048876.114. Epub 2015 Jul 2. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26137849 Free PMC article.
-
Sweating the small stuff: microRNAs and genetic changes define pancreatic cancer.Pancreas. 2013 Jul;42(5):740-59. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182854ab0. Pancreas. 2013. PMID: 23774697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA virus microRNA that mimics a B-cell oncomiR.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 21;109(8):3077-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1116107109. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22308400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros, V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350-355. - PubMed
-
- An, F. Q., H. M. Folarin, N. Compitello, J. Roth, S. L. Gerson, K. R. McCrae, F. D. Fakhari, D. P. Dittmer, and R. Renne. 2006. Long-term-infected telomerase-immortalized endothelial cells: a model for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 80:4833-4846. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartel, D. P. 2004. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281-297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

