Arkadia activates Smad3/Smad4-dependent transcription by triggering signal-induced SnoN degradation
- PMID: 17591695
- PMCID: PMC1952153
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00664-07
Arkadia activates Smad3/Smad4-dependent transcription by triggering signal-induced SnoN degradation
Abstract
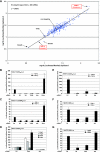
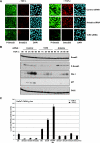
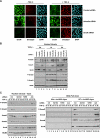
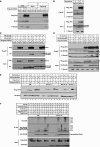
E3 ubiquitin ligases play important roles in regulating transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)/Smad signaling. Screening of an E3 ubiquitin ligase small interfering RNA library, using TGF-beta induction of a Smad3/Smad4-dependent luciferase reporter as a readout, revealed that Arkadia is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that is absolutely required for this TGF-beta response. Knockdown of Arkadia or overexpression of a dominant-negative mutant completely abolishes transcription from Smad3/Smad4-dependent reporters, but not from Smad1/Smad4-dependent reporters or from reporters driven by Smad2/Smad4/FoxH1 complexes. We show that Arkadia specifically activates transcription via Smad3/Smad4 binding sites by inducing degradation of the transcriptional repressor SnoN. Arkadia is essential for TGF-beta-induced SnoN degradation, but it has little effect on SnoN levels in the absence of signal. Arkadia interacts with SnoN and induces its ubiquitination irrespective of TGF-beta/Activin signaling, but SnoN is efficiently degraded only when it forms a complex with both Arkadia and phosphorylated Smad2 or Smad3. Finally, we describe an esophageal cancer cell line (SEG-1) that we show has lost Arkadia expression and is deficient for SnoN degradation. Reintroduction of wild-type Arkadia restores TGF-beta-induced Smad3/Smad4-dependent transcription and SnoN degradation in these cells, raising the possibility that loss of Arkadia function may be relevant in cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Requirement for the SnoN oncoprotein in transforming growth factor beta-induced oncogenic transformation of fibroblast cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(24):10731-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.10731-10744.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16314499 Free PMC article.
-
Arkadia induces degradation of SnoN and c-Ski to enhance transforming growth factor-beta signaling.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jul 13;282(28):20492-501. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701294200. Epub 2007 May 16. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17510063
-
The four and a half LIM-only protein 2 (FHL2) activates transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling by regulating ubiquitination of the E3 ligase Arkadia.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 18;288(3):1785-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.439760. Epub 2012 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23212909 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of TGF-beta family signaling by E3 ubiquitin ligases.Cancer Sci. 2008 Nov;99(11):2107-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00925.x. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18808420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SnoN in TGF-beta signaling and cancer biology.Curr Mol Med. 2008 Jun;8(4):319-28. doi: 10.2174/156652408784533797. Curr Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18537639 Review.
Cited by
-
TGFβ signalling in context.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;13(10):616-30. doi: 10.1038/nrm3434. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22992590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Proteomics of the SMAD (Suppressor of Mothers against Decapentaplegic) Transcription Factor Family Identifies Importin 5 as a Bone Morphogenic Protein Receptor SMAD-specific Importin.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 11;291(46):24121-24132. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.748582. Epub 2016 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27703004 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular variation in signaling through the TGF-β pathway and its relation to cell density and cell cycle phase.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Jul;11(7):M111.013482. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.013482. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22442258 Free PMC article.
-
Key role for ubiquitin protein modification in TGFβ signal transduction.Ups J Med Sci. 2012 May;117(2):153-65. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2012.654858. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Ups J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22335355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SNW1 is a critical regulator of spatial BMP activity, neural plate border formation, and neural crest specification in vertebrate embryos.PLoS Biol. 2011 Feb 15;9(2):e1000593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000593. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21358802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonni, S., H. R. Wang, C. G. Causing, P. Kavsak, S. L. Stroschein, K. Luo, and J. L. Wrana. 2001. TGF-β induces assembly of a Smad2-Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase complex that targets SnoN for degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:587-595. - PubMed
-
- Boyer, P. L., C. Colmenares, E. Stavnezer, and S. H. Hughes. 1993. Sequence and biological activity of chicken snoN cDNA clones. Oncogene 8:457-466. - PubMed
-
- Chen, X., M. J. Rubock, and M. Whitman. 1996. A transcriptional partner for MAD proteins in TGF-β signalling. Nature 383:691-696. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, S. B., R. Nicol, and E. Stavnezer. 1998. A domain necessary for the transforming activity of SnoN is required for specific DNA binding, transcriptional repression and interaction with TAF(II)110. Oncogene 17:2505-2513. - PubMed
-
- Dennler, S., S. Huet, and J. M. Gauthier. 1999. A short amino-acid sequence in MH1 domain is responsible for functional differences between Smad2 and Smad3. Oncogene 18:1643-1648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
