No correlation exists between disease activity and the expression of killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17497034
- PMCID: PMC1804296
- DOI: 10.1155/2007/65179
No correlation exists between disease activity and the expression of killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: The genes for killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) have been cloned and their functions and expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have been partially clarified. However, the correlation between their expression and disease activity has not been analyzed in patients with RA. Thus, we measured KIR expression on lymphocytes in patients with RA, and assessed the correlation between KIR expression and disease activity.
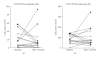
Patients and methods: In the cross-sectional study, 15 patients (9 females and 6 males) who fulfilled the diagnostic criteria for RA were assessed. In the longitudinal study, patients who were followed-up for 3 months were assessed. CD158a/b expression on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of RA patients was analyzed using flow cytometry.
Results: No significant correlation between KIR expression and CRP, ESR, or IgM-RF was observed. There was no remarkable change in the expression of KIRs between the baseline and after 3 months. Additionally, in the 5 patients whose expression of KIRs particularly changed, the time-related changes in the expression of KIRs were independent from those of inflammation parameters and IgM-RF.
Conclusion: There was no correlation between KIR expression and disease activity; therefore, the clinical use of KIR expression should be limited, while unnatural KIR expression may be involved in the pathogenesis of RA, but not a recruitment of chronic inflammation to induce joint damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of interleukin 2 on killer cell inhibitory receptors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Feb;60(2):166-9. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.2.166. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001. PMID: 11156551 Free PMC article.
-
[Immunoediting of natural killer cells by human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line: altered expression of KIRs and NKG2D receptors leads to reduction of natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Mar;27(3):247-9. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17425963 Chinese.
-
Natural killer cytolytic activity is associated with the expression of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors on peripheral lymphocytes in human.Mediators Inflamm. 2003 Apr;12(2):117-21. doi: 10.1080/0962935031000097727. Mediators Inflamm. 2003. PMID: 12775362 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of killer cell immunoglobulin like receptors with rheumatoid arthritis among North Indian population.Hum Immunol. 2014 Aug;75(8):802-7. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2014.05.014. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Hum Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24912006
-
Associations of killer cell immunoglobulin- like receptor genes with rheumatoid arthritis.Dis Markers. 2012;33(4):201-6. doi: 10.3233/DMA-2012-0927. Dis Markers. 2012. PMID: 22960345 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility Is Associated with the KIR2DS4-Full of Killer-Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor Genes in the Lur Population of Iran.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Apr;10(1):84-94. doi: 10.52547/rbmb.10.1.84. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34277872 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Killer Cell Immunoglobulin- Like Receptor Genes in Iranian Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0143757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143757. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26658904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wagtmann N, Biassoni R, Cantoni C, et al. Molecular clones of the p58 NK cell receptor reveal immunoglobulin-related molecules with diversity in both the extra- and intracellular domains. Immunity. 1995;2(5):439–449. - PubMed
-
- Colonna M, Samaridis J. Cloning of immunoglobulin-superfamily members associated with HLA-C and HLA-B recognition by human natural killer cells. Science. 1995;268(5209):405–408. - PubMed
-
- D'Andrea A, Chang C, Franz-Bacon K, McClanahan T, Phillips JH, Lanier LL. Molecular cloning of NKB1 a natural killer cell receptor for HLA-B allotypes. Journal of Immunology. 1995;155(5):2306–2310. - PubMed
-
- Binstadt BA, Brumbaugh KM, Dick CJ, et al. Sequential involvement of Lck and SHP-1 with MHC-recognizing receptors on NK cells inhibits FcR-initiated tyrosine kinase activation. Immunity. 1996;5(6):629–638. - PubMed
-
- Vivier E, Daëron M. Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs. Immunology Today. 1997;18(6):286–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

