Reactivation of the p53 pathway as a treatment modality for KSHV-induced lymphomas
- PMID: 17364023
- PMCID: PMC1810577
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30945
Reactivation of the p53 pathway as a treatment modality for KSHV-induced lymphomas
Abstract
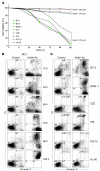
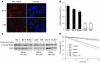
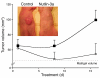
Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV) is the etiologic agent for primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), a non-Hodgkin type lymphoma manifesting as an effusion malignancy in the affected individual. Although KSHV has been recognized as a tumor virus for over a decade, the pathways for its tumorigenic conversion are incompletely understood, which has greatly hampered the development of efficient therapies for KSHV-induced malignancies like PEL and Kaposi's sarcoma. There are no current therapies effective against the aggressive, KSHV-induced PEL. Here we demonstrate that activation of the p53 pathway using murine double minute 2 (MDM2) inhibitor Nutlin-3a conveyed specific and highly potent activation of PEL cell killing. Our results demonstrated that the KSHV latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA) bound to both p53 and MDM2 and that the MDM2 inhibitor Nutlin-3a disrupted the p53-MDM2-LANA complex and selectively induced massive apoptosis in PEL cells. Together with our results indicating that KSHV-infection activated DNA damage signaling, these findings contribute to the specificity of the cytotoxic effects of Nutlin-3a in KSHV-infected cells. Moreover, we showed that Nutlin-3a had striking antitumor activity in vivo in a mouse xenograft model. Our results therefore present new options for exploiting reactivation of p53 as what we believe to be a novel and highly selective treatment modality for this virally induced lymphoma.
Figures


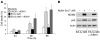

Similar articles
-
p53 reactivation kills KSHV lymphomas efficiently in vitro and in vivo: new hope for treating aggressive viral lymphomas.Cell Cycle. 2007 Sep 15;6(18):2205-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.18.4730. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17890905 Review.
-
Repurposing Cytarabine for Treating Primary Effusion Lymphoma by Targeting Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latent and Lytic Replications.mBio. 2018 May 8;9(3):e00756-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00756-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29739902 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus lytic replication compromises apoptotic response to p53 reactivation in virus-induced lymphomas.Oncogene. 2013 Feb 28;32(9):1091-8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.118. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22469985
-
Activated Nrf2 Interacts with Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency Protein LANA-1 and Host Protein KAP1 To Mediate Global Lytic Gene Repression.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7874-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00895-15. Epub 2015 May 20. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25995248 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Features of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1045:357-376. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7230-7_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29896675 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression Ratios of the Antiapoptotic BCL2 Family Members Dictate the Selective Addiction of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Transformed Primary Effusion Lymphoma Cell Lines to MCL1.J Virol. 2022 Dec 14;96(23):e0136022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01360-22. Epub 2022 Nov 23. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36416587 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Abundance of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF50 Protein by Oncoprotein MDM2.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Oct 3;12(10):e1005918. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005918. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27698494 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel p53 pathway activating small-molecule compounds reveals unexpected similarities with known therapeutic agents.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 27;5(9):e12996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012996. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20885994 Free PMC article.
-
A human herpesvirus microRNA inhibits p21 expression and attenuates p21-mediated cell cycle arrest.J Virol. 2010 May;84(10):5229-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00202-10. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20219912 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Dispiro-Indolinones with Anticancer Activity.Molecules. 2023 Jan 30;28(3):1325. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031325. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang Y., et al. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865–1869. - PubMed
-
- Soulier J., et al. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman’s disease. Blood. 1995;86:1276–1280. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E., et al. In vitro establishment and characterization of two acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related lymphoma cell lines (BC-1 and BC-2) containing Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like (KSHV) DNA sequences. Blood. 1995;86:2708–2714. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E., Knowles D.M. The role of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) in lymphoproliferative diseases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1999;9:165–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

