The delayed effects of chronic unpredictable stress on anxiety measures
- PMID: 17275043
- PMCID: PMC1931411
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.12.006
The delayed effects of chronic unpredictable stress on anxiety measures
Abstract
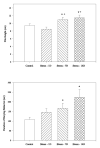
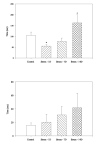
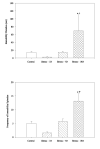
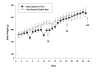
Previous research has found that exposure to unpredictable stress can augment anxiety in humans and animals. The appearance of anxiety symptoms in humans frequently develop after stress exposure has terminated, but few rodent studies have systematically examined the delayed anxiogenic effects of unpredictable stress. Therefore, the current study investigated whether anxiety-like behaviors in rats would increase at several time intervals following exposure to chronic unpredictable stress (CUS). Unconditioned and conditioned response tasks were used to assess anxiety in male rats 1, 7 or 14 days following exposure to 10 days of a variety of stressors. Rats exposed to CUS showed increased burying behaviors and immobility during the defensive burying test, a conditioned anxiety test. The effects on burying behavior were apparent 7 and 14 days after the termination of the unpredictable stress procedure, but not when tested 1 day after CUS. Total time immobile in the defensive burying test also increased 14 days after termination of the last stressor. In contrast, there were no significant effects of CUS on behavioral measures in the unconditioned response tasks, the elevated plus-maze or light-dark box, at any time point following exposure to CUS. The current findings suggest that CUS may be a useful model of human conditioned anxiety that develops subsequent to chronic stress exposure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of chronic unpredictable stress on male rats in the water maze.Physiol Behav. 2005 Sep 15;86(1-2):21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.06.027. Physiol Behav. 2005. PMID: 16099481
-
Noradrenergic facilitation of shock-probe defensive burying in lateral septum of rats, and modulation by chronic treatment with desipramine.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Mar 30;31(2):482-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2006.11.015. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17188790
-
Sex-dependent effects of chronic unpredictable stress in the water maze.Physiol Behav. 2011 Mar 1;102(3-4):266-75. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.10.022. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Physiol Behav. 2011. PMID: 21056052
-
Modulation of different states of anxiety-like behavior by chronic stress.Behav Neurosci. 2004 Dec;118(6):1450-4. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.118.6.1450. Behav Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15598155
-
Tests of unconditioned anxiety - pitfalls and disappointments.Physiol Behav. 2014 Aug;135:55-71. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.05.032. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Physiol Behav. 2014. PMID: 24910138 Review.
Cited by
-
Antidepressant Effects of Ketamine Are Not Related to ¹⁸F-FDG Metabolism or Tyrosine Hydroxylase Immunoreactivity in the Ventral Tegmental Area of Wistar Rats.Neurochem Res. 2015 Jun;40(6):1153-64. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1576-3. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25894683
-
Enhanced fear recall and emotional arousal in rats recovering from chronic variable stress.Physiol Behav. 2010 Nov 2;101(4):474-82. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.07.013. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Physiol Behav. 2010. PMID: 20678511 Free PMC article.
-
Gender-specific impact of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling on stress-induced depression-like behavior.Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Jul 1;66(1):84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.02.007. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19358977 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Stress Alters Behavior in the Forced Swim Test and Underlying Neural Activity in Animals Exposed to Alcohol Prenatally: Sex- and Time-Dependent Effects.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Mar 9;12:42. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00042. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29593510 Free PMC article.
-
Reproductive tract extracellular vesicles are sufficient to transmit intergenerational stress and program neurodevelopment.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 20;11(1):1499. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15305-w. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32198406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamec R, Head D, Blundell J, Burton P, Berton O. Lasting anxiogenic effects of feline predator stress in mice: Sex differences in vulnerability to stress and predicting severity of anxiogenic responses from the stress experience. Physiol Behav. 2006;88:12–29. - PubMed
-
- Adamec R, Walling S, Burton P. Long-lasting, selective, anxiogenic effects of feline predator stress in mice. Physiol Behav. 2004;83:401–410. - PubMed
-
- Adamec RE. Stress effects on limbic function and behavior. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003;27:1173–1175. - PubMed
-
- Adamec RE, Blundell J, Collins A. Neural plasticity and stress induced changes in defense in the rat. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2001;25:721–744. - PubMed
-
- Adamec RE, Shallow T. Lasting effects on rodent anxiety of a single exposure to a cat. Physiol Behav. 1993;54:101–109. - PubMed

