Rescue of TRAF3-null mice by p100 NF-kappa B deficiency
- PMID: 17015635
- PMCID: PMC2118128
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20061166
Rescue of TRAF3-null mice by p100 NF-kappa B deficiency
Abstract
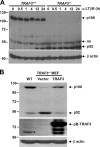
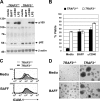
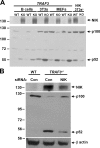
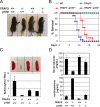
Proper activation of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB transcription factors is critical in regulating fundamental biological processes such as cell survival and proliferation, as well as in inflammatory and immune responses. Recently, the NF-kappaB signaling pathways have been categorized into the canonical pathway, which results in the nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB complexes containing p50, and the noncanonical pathway, which involves the induced processing of p100 to p52 and the formation of NF-kappaB complexes containing p52 (Bonizzi, G., and M. Karin. 2004. Trends Immunol. 25:280-288). We demonstrate that loss of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3) results in constitutive noncanonical NF-kappaB activity. Importantly, TRAF3-/- B cells show ligand-independent up-regulation of intracellular adhesion molecule 1 and protection from spontaneous apoptosis during in vitro culture. In addition, we demonstrate that loss of TRAF3 results in profound accumulation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase in TRAF3-/- cells. Finally, we show that the early postnatal lethality observed in TRAF3-deficient mice is rescued by compound loss of the noncanonical NF-kappaB p100 gene. Thus, these genetic data clearly demonstrate that TRAF3 is a critical negative modulator of the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway and that constitutive activation of the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway causes the lethal phenotype of TRAF3-deficient mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specificity of TRAF3 in its negative regulation of the noncanonical NF-kappa B pathway.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 9;282(6):3688-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610271200. Epub 2006 Dec 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17158868
-
NF-kappaB p100 limits TNF-induced bone resorption in mice by a TRAF3-dependent mechanism.J Clin Invest. 2009 Oct;119(10):3024-34. doi: 10.1172/JCI38716. Epub 2009 Sep 21. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19770515 Free PMC article.
-
Control of canonical NF-kappaB activation through the NIK-IKK complex pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Mar 4;105(9):3503-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707959105. Epub 2008 Feb 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18292232 Free PMC article.
-
The noncanonical NF-κB pathway.Immunol Rev. 2012 Mar;246(1):125-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01088.x. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22435551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAF3 and its biological function.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;597:48-59. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-70630-6_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17633016 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through TRAF3-mediated suppression of interleukin 17 receptor signaling.J Exp Med. 2010 Nov 22;207(12):2647-62. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100703. Epub 2010 Nov 15. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 21078888 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical NF-κB signaling is limited by classical NF-κB activity.Sci Signal. 2014 Feb 4;7(311):ra13. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004557. Sci Signal. 2014. PMID: 24497610 Free PMC article.
-
Hexavalent chromium exposure activates the non-canonical nuclear factor kappa B pathway to promote immune checkpoint protein programmed death-ligand 1 expression and lung carcinogenesis.Cancer Lett. 2024 May 1;589:216827. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216827. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Cancer Lett. 2024. PMID: 38527692 Free PMC article.
-
Hodgkin lymphoma requires stabilized NIK and constitutive RelB expression for survival.Blood. 2012 Nov 1;120(18):3756-63. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-405951. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22968463 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF3 Modulation: Novel Mechanism for the Anti-inflammatory Effects of the Vitamin D Receptor Agonist Paricalcitol in Renal Disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Sep;31(9):2026-2042. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019111206. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32631974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonizzi, G., and M. Karin. 2004. The two NF-kappaB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 25:280–288. - PubMed
-
- Hayden, M.S., and S. Ghosh. 2004. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Karin, M., and Y. Ben-Neriah. 2000. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18:621–663. - PubMed
-
- Xiao, G., E.W. Harhaj, and S.C. Sun. 2001. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. Mol. Cell. 7:401–409. - PubMed
-
- Dejardin, E., N.M. Droin, M. Delhase, E. Haas, Y. Cao, C. Makris, Z.W. Li, M. Karin, C.F. Ware, and D.R. Green. 2002. The lymphotoxin-beta receptor induces different patterns of gene expression via two NF-kappaB pathways. Immunity. 17:525–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

