Fusion-induced apoptosis contributes to thymocyte depletion by a pathogenic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope in the human thymus
- PMID: 16956934
- PMCID: PMC1642149
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01382-06
Fusion-induced apoptosis contributes to thymocyte depletion by a pathogenic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope in the human thymus
Abstract
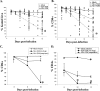
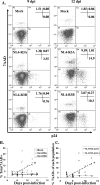
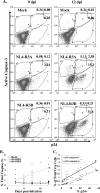
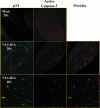
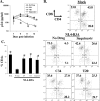
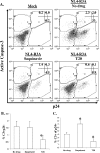
The mechanisms of CD4(+) T-cell depletion during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection remain incompletely characterized. Of particular importance is how CD4(+) T cells are depleted within the lymphoid organs, including the lymph nodes and thymus. Herein we characterize the pathogenic mechanisms of an envelope from a rapid progressor (R3A Env) in the NL4-3 backbone (NL4-R3A) which is able to efficiently replicate and deplete CD4(+) thymocytes in the human fetal-thymus organ culture (HF-TOC). We demonstrate that uninterrupted replication is required for continual thymocyte depletion. During depletion, NL4-R3A induces an increase in thymocytes which uptake 7AAD, a marker of cell death, and which express active caspase-3, a marker of apoptosis. While 7AAD uptake is observed predominantly in uninfected thymocytes (p24(-)), active caspase-3 is expressed in both infected (p24(+)) and uninfected thymocytes (p24(-)). When added to HF-TOC with ongoing infection, the protease inhibitor saquinavir efficiently suppresses NL4-R3A replication. In contrast, the fusion inhibitors T20 and C34 allow for sustained HIV-1 production. Interestingly, T20 and C34 effectively prevent thymocyte depletion in spite of this sustained replication. Apoptosis of both p24(-) and p24(+) thymocytes appears to be envelope fusion dependent, as T20, but not saquinavir, is capable of reducing thymocyte apoptosis. Together, our data support a model whereby pathogenic envelope-dependent fusion contributes to thymocyte depletion in HIV-1-infected thymus, correlated with induction of apoptosis in both p24(+) and p24(-) thymocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Using Experience Sampling Methodology to Capture Disclosure Opportunities for Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):389-400. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0090. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116059 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological treatments in panic disorder in adults: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 28;11(11):CD012729. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012729.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38014714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preferential cytolysis of peripheral memory CD4+ T cells by in vitro X4-tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection before the completion of reverse transcription.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(18):9154-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00773-08. Epub 2008 Jul 2. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18596085 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Pathogenicity of SHIV KB9 and 89.6 Env Correlates with Bystander Apoptosis Induction in CD4+ T cells.Viruses. 2019 Oct 1;11(10):911. doi: 10.3390/v11100911. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31581579 Free PMC article.
-
Type I interferon contributes to CD4+ T cell depletion induced by infection with HIV-1 in the human thymus.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(17):9243-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00457-11. Epub 2011 Jun 22. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21697497 Free PMC article.
-
V3 loop truncations in HIV-1 envelope impart resistance to coreceptor inhibitors and enhanced sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies.PLoS Pathog. 2007 Aug 24;3(8):e117. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030117. PLoS Pathog. 2007. PMID: 17722977 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting HIV-1 gp41-induced fusion and pathogenesis for anti-viral therapy.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011 Dec;11(24):2947-58. doi: 10.2174/156802611798808479. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 22044225 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alimonti, J. B., T. B. Ball, and K. R. Fowke. 2003. Mechanisms of CD4+ T lymphocyte cell death in human immunodeficiency virus infection and AIDS. J. Gen. Virol. 84:1649-1661. - PubMed
-
- Biard-Piechaczyk, M., V. Robert-Hebmann, V. Richard, J. Roland, R. A. Hipskind, and C. Devaux. 2000. Caspase-dependent apoptosis of cells expressing the chemokine receptor CXCR4 is induced by cell membrane-associated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein (gp120). Virology 268:329-344. - PubMed
-
- Bonyhadi, M. L., L. Rabin, S. Salimi, D. A. Brown, J. Kosek, J. M. McCune, and H. Kaneshima. 1993. HIV induces thymus depletion in vivo. Nature 363:728-732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

