Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus LANA-1 interacts with the short variant of BRD4 and releases cells from a BRD4- and BRD2/RING3-induced G1 cell cycle arrest
- PMID: 16928766
- PMCID: PMC1641788
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00804-06
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus LANA-1 interacts with the short variant of BRD4 and releases cells from a BRD4- and BRD2/RING3-induced G1 cell cycle arrest
Abstract
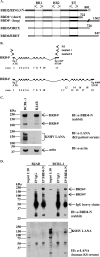
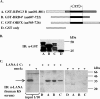
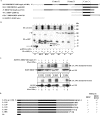
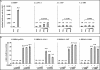
The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) latency-associated nuclear antigen 1 (LANA-1) is required for the replication of episomal viral genomes. Regions in its N-terminal and C-terminal domains mediate the interaction with host cell chromatin. Several cellular nuclear proteins, e.g., BRD2/RING3, histones H2A and H2B, MeCP2, DEK, and HP1alpha, have been suggested to mediate this interaction. In this work, we identify the double-bromodomain proteins BRD4 and BRD3/ORFX as additional LANA-1 interaction partners. The carboxy-terminal region of the short variant of BRD4 (BRD4S) containing the highly conserved extraterminal domain directly interacts with an element in the LANA-1 carboxy-terminal domain. We show that ectopically expressed BRD4S and BRD2/RING3 delay progression into the S phase of the cell cycle in epithelial and B-cell lines and increase cyclin E promoter activity. LANA-1 partly releases epithelial and B cells from a BRD4S- and BRD2/RING3-induced G1 cell cycle arrest and also promotes S-phase entry in the presence of BRD4S and BRD2/RING3. This is accompanied by a reduction in BRD4S-mediated cyclin E promoter activity. Our data are in keeping with the notion that the direct interaction of KSHV LANA-1 with BRD4 and other BRD proteins could play a role in the G1/S phase-promoting functions of KSHV LANA-1. Further, our data support a model in which the LANA-1 C terminus contributes to a functional attachment to acetylated histones H3 and H4 via BRD4 and BRD2, in addition to the recently demonstrated direct interaction (A. J. Barbera, J. V. Chodaparambil, B. Kelley-Clarke, V. Joukov, J. C. Walter, K. Luger, and K. M. Kaye, Science 311:856-861, 2006) of the LANA-1 N terminus with histones H2A and H2B.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen interacts with bromodomain protein Brd4 on host mitotic chromosomes.J Virol. 2006 Sep;80(18):8909-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00502-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16940503 Free PMC article.
-
Brd2/RING3 interacts with a chromatin-binding domain in the Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen 1 (LANA-1) that is required for multiple functions of LANA-1.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(21):13618-29. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.21.13618-13629.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16227282 Free PMC article.
-
Bub1 in Complex with LANA Recruits PCNA To Regulate Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latent Replication and DNA Translesion Synthesis.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10206-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01524-15. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26223641 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of latency-associated nuclear antigen.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;312:101-36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34344-8_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17089795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency-Associated Nuclear Antigen: Replicating and Shielding Viral DNA during Viral Persistence.J Virol. 2017 Jun 26;91(14):e01083-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01083-16. Print 2017 Jul 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28446671 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Viral Manipulation of the Host Epigenome as a Driver of Virus-Induced Oncogenesis.Microorganisms. 2021 May 30;9(6):1179. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061179. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34070716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of viral cis elements conferring Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus episome partitioning and maintenance.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(18):9825-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00842-07. Epub 2007 Jul 11. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17626102 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biology of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and related oncogenesis.Adv Virus Res. 2010;78:87-142. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385032-4.00003-3. Adv Virus Res. 2010. PMID: 21040832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MLL1 is regulated by KSHV LANA and is important for virus latency.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Dec 16;49(22):12895-12911. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1094. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34850113 Free PMC article.
-
Triple lysine and nucleosome-binding motifs of the viral IE19 protein are required for human cytomegalovirus S-phase infections.mBio. 2024 Jun 12;15(6):e0016224. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00162-24. Epub 2024 May 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38695580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An, F. Q., N. Compitello, E. Horwitz, M. Sramkoski, E. S. Knudsen, and R. Renne. 2005. The latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus modulates cellular gene expression and protects lymphoid cells from p16 INK4A-induced cell cycle arrest. J. Biol. Chem. 280:3862-3874. - PubMed
-
- Barbera, A. J., J. V. Chodaparambil, B. Kelley-Clarke, V. Joukov, J. C. Walter, K. Luger, and K. M. Kaye. 2006. The nucleosomal surface as a docking station for Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus LANA. Science 311:856-861. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman, E., Y. Chang, P. S. Moore, J. W. Said, and D. M. Knowles. 1995. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:1186-1191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

