Type 2 immunity is controlled by IL-4/IL-13 expression in hematopoietic non-eosinophil cells of the innate immune system
- PMID: 16702603
- PMCID: PMC2118302
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20052448
Type 2 immunity is controlled by IL-4/IL-13 expression in hematopoietic non-eosinophil cells of the innate immune system
Erratum in
- J Exp Med. 2006 Jun 12;203(6):1617
Abstract
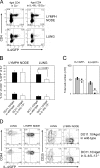
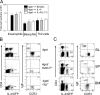
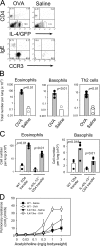
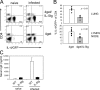
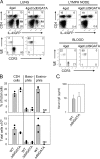
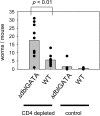
Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection and ovalbumin-induced allergic lung pathology are highly interleukin (IL)-4/IL-13 dependent, but the contributions of IL-4/IL-13 from adaptive (T helper [Th]2 cells) and innate (eosinophil, basophils, and mast cells) immune cells remain unknown. Although required for immunoglobulin (Ig)E induction, IL-4/IL-13 from Th2 cells was not required for worm expulsion, tissue inflammation, or airway hyperreactivity. In contrast, innate hematopoietic cell-derived IL-4/IL-13 was dispensable for Th2 cell differentiation in lymph nodes but required for effector cell recruitment and tissue responses. Eosinophils were not required for primary immune responses. Thus, components of type 2 immunity mediated by IL-4/IL-13 are partitioned between T cell-dependent IgE and an innate non-eosinophil tissue component, suggesting new strategies for interventions in allergic immunity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-4-promoted T helper 2 responses enhance Nippostrongylus brasiliensis-induced pulmonary pathology.Infect Immun. 2008 Dec;76(12):5535-42. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00210-08. Epub 2008 Sep 22. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18809669 Free PMC article.
-
Basophil-mediated protection against gastrointestinal helminths requires IgE-induced cytokine secretion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 2;111(48):E5169-77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1412663111. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25404305 Free PMC article.
-
Protective roles of eosinophils in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997 Oct;114 Suppl 1:45-50. doi: 10.1159/000237717. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9363925
-
Basophils: emerging roles in the pathogenesis of allergic disease.Immunol Rev. 2011 Jul;242(1):144-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01023.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21682743 Review.
-
Regulation of type 2 immunity by basophils.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;785:37-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-6217-0_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23456835 Review.
Cited by
-
Single cell analysis of host response to helminth infection reveals the clonal breadth, heterogeneity, and tissue-specific programming of the responding CD4+ T cell repertoire.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jun 9;17(6):e1009602. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009602. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34106992 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent expression patterns of IL-4 and IL-13 define unique functions in allergic immunity.Nat Immunol. 2011 Dec 4;13(1):58-66. doi: 10.1038/ni.2182. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22138715 Free PMC article.
-
What Can Parasites Tell Us About the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Asthma and Allergic Diseases.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 11;11:2106. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02106. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depletion of major pathogenic cells in asthma by targeting CRTh2.JCI Insight. 2016 May 19;1(7):e86689. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.86689. JCI Insight. 2016. PMID: 27699264 Free PMC article.
-
Basophils as Key Regulators of Allergic Inflammation and Th2-type Immunity.World Allergy Organ J. 2008 Jul;1(7):123-8. doi: 10.1097/WOX.0b013e31817a76fb. World Allergy Organ J. 2008. PMID: 23282479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cliffe, L.J., N.E. Humphreys, T.E. Lane, C.S. Potten, C. Booth, and R.K. Grencis. 2005. Accelerated intestinal epithelial cell turnover: a new mechanism of parasite expulsion. Science. 308:1463–1465. - PubMed
-
- Finkelman, F.D., T. Shea-Donohue, S.C. Morris, L. Gildea, R. Strait, K.B. Madden, L. Schopf, and J.F. Urban Jr. 2004. Interleukin-4- and interleukin-13-mediated host protection against intestinal nematode parasites. Immunol. Rev. 201:139–155. - PubMed
-
- Voehringer, D., K. Shinkai, and R.M. Locksley. 2004. Type 2 immunity reflects orchestrated recruitment of cells committed to IL-4 production. Immunity. 20:267–277. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham, A.F., P.G. Fallon, M. Khan, S. Vacheron, H. Acha-Orbea, I.C. MacLennan, A.N. McKenzie, and K.M. Toellner. 2002. Th2 activities induced during virgin T cell priming in the absence of IL-4, IL-13, and B cells. J. Immunol. 169:2900–2906. - PubMed
-
- Urban, J.F., Jr., C.R. Maliszewski, K.B. Madden, I.M. Katona, and F.D. Finkelman. 1995. IL-4 treatment can cure established gastrointestinal nematode infections in immunocompetent and immunodeficient mice. J. Immunol. 154:4675–4684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

