Genome-wide gene expression in response to parasitoid attack in Drosophila
- PMID: 16277749
- PMCID: PMC1297650
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-11-r94
Genome-wide gene expression in response to parasitoid attack in Drosophila
Abstract
Background: Parasitoids are insect parasites whose larvae develop in the bodies of other insects. The main immune defense against parasitoids is encapsulation of the foreign body by blood cells, which subsequently often melanize. The capsule sequesters and kills the parasite. The molecular processes involved are still poorly understood, especially compared with insect humoral immunity.
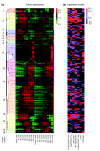
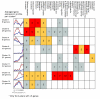
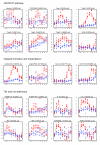
Results: We explored the transcriptional response to parasitoid attack in Drosophila larvae at nine time points following parasitism, hybridizing five biologic replicates per time point to whole-genome microarrays for both parasitized and control larvae. We found significantly different expression profiles for 159 probe sets (representing genes), and we classified them into 16 clusters based on patterns of co-expression. A series of functional annotations were nonrandomly associated with different clusters, including several involving immunity and related functions. We also identified nonrandom associations of transcription factor binding sites for three main regulators of innate immune responses (GATA/srp-like, NF-kappaB/Rel-like and Stat), as well as a novel putative binding site for an unknown transcription factor. The appearance or absence of candidate genes previously associated with insect immunity in our differentially expressed gene set was surveyed.
Conclusion: Most genes that exhibited altered expression following parasitoid attack differed from those induced during antimicrobial immune responses, and had not previously been associated with defense. Applying bioinformatic techniques contributed toward a description of the encapsulation response as an integrated system, identifying putative regulators of co-expressed and functionally related genes. Genome-wide studies such as ours are a powerful first approach to investigating novel genes involved in invertebrate immunity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inter- and intra-species variation in genome-wide gene expression of Drosophila in response to parasitoid wasp attack.BMC Genomics. 2017 Apr 27;18(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3697-3. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28449654 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomics of the evolution of increased resistance to parasitism in Drosophila.Mol Ecol. 2011 Mar;20(5):932-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04911.x. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Mol Ecol. 2011. PMID: 21062384
-
Cellular and humoral immune interactions between Drosophila and its parasitoids.Insect Sci. 2021 Oct;28(5):1208-1227. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12863. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Insect Sci. 2021. PMID: 32776656 Review.
-
JAK/STAT signaling in Drosophila muscles controls the cellular immune response against parasitoid infection.EMBO Rep. 2015 Dec;16(12):1664-72. doi: 10.15252/embr.201540277. Epub 2015 Sep 27. EMBO Rep. 2015. PMID: 26412855 Free PMC article.
-
Immune resistance of Drosophila hosts against Asobara parasitoids: cellular aspects.Adv Parasitol. 2009;70:189-215. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(09)70007-7. Adv Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19773071 Review.
Cited by
-
Contrasting infection strategies in generalist and specialist wasp parasitoids of Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Pathog. 2007 Oct 26;3(10):1486-501. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030158. PLoS Pathog. 2007. PMID: 17967061 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome changes in the plasma of Papilio xuthus (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae): effect of parasitization by the endoparasitic wasp Pteromalus puparum (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae).J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2009 Jun;10(6):445-53. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B0820314. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2009. PMID: 19489110 Free PMC article.
-
Demonstration of cytotoxicity against wasps by pierisin-1: a possible defense factor in the cabbage white butterfly.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 23;8(4):e60539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060539. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23637752 Free PMC article.
-
Edin Expression in the Fat Body Is Required in the Defense Against Parasitic Wasps in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Pathog. 2015 May 12;11(5):e1004895. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004895. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25965263 Free PMC article.
-
Disease induced dynamics in host-parasitoid systems: chaos and coexistence.J R Soc Interface. 2007 Jun 22;4(14):463-71. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2006.0184. J R Soc Interface. 2007. PMID: 17251140 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

