Deletion of SOCS7 leads to enhanced insulin action and enlarged islets of Langerhans
- PMID: 16127460
- PMCID: PMC1190369
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23853
Deletion of SOCS7 leads to enhanced insulin action and enlarged islets of Langerhans
Abstract
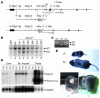
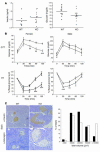
NIDDM is characterized by progressive insulin resistance and the failure of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells to compensate for this resistance. Hyperinsulinemia, inflammation, and prolonged activation of the insulin receptor (INSR) have been shown to induce insulin resistance by decreasing INSR substrate (IRS) protein levels. Here we describe a role for SOCS7 in regulating insulin signaling. Socs7-deficient mice exhibited lower glucose levels and prolonged hypoglycemia during an insulin tolerance test and increased glucose clearance in a glucose tolerance test. Six-month-old Socs7-deficient mice exhibited increased growth of pancreatic islets with mildly increased fasting insulin levels and hypoglycemia. These defects correlated with increased IRS protein levels and enhanced insulin action in cells lacking SOCS7. Additionally, SOCS7 associated with the INSR and IRS1--molecules that are essential for normal regulation of insulin action. These data suggest that SOCS7 is a potent regulator of glucose homeostasis and insulin signaling.
Figures
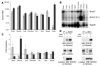
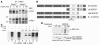
Similar articles
-
Disruption of the SH2-B gene causes age-dependent insulin resistance and glucose intolerance.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;24(17):7435-43. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7435-7443.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15314154 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice.Nature. 1998 Feb 26;391(6670):900-4. doi: 10.1038/36116. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9495343
-
Disruption of insulin receptor substrate 2 causes type 2 diabetes because of liver insulin resistance and lack of compensatory beta-cell hyperplasia.Diabetes. 2000 Nov;49(11):1880-9. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.11.1880. Diabetes. 2000. PMID: 11078455
-
Molecular insights into insulin action and secretion.Eur J Clin Invest. 2002 Jun;32 Suppl 3:3-13. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.32.s3.2.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12028370 Review.
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
Cited by
-
The Neglected Suppressor of Cytokine Signalling (SOCS): SOCS4-7.Inflammation. 2024 Oct 26. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02163-7. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39460806 Review.
-
Inflammatory Skin Diseases: Focus on the Role of Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling (SOCS) Proteins.Cells. 2024 Mar 13;13(6):505. doi: 10.3390/cells13060505. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetogenic viruses: linking viruses to diabetes mellitus.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 30;9(4):e15021. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15021. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37064445 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SOCS and VHL Proteins in Neuronal Differentiation and Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 15;24(4):3880. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043880. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 22;14(10):2549. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102549. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rice KM, Turnbow MA, Garner CW. Insulin stimulates the degradation of IRS-1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993;190:961–967. - PubMed
-
- Sun XJ, Goldberg JL, Qiao LY, Mitchell JJ. Insulin-induced insulin receptor substrate-1 degradation is mediated by the proteasome degradation pathway. Diabetes. 1999;48:1359–1364. - PubMed
-
- Senn JJ, Klover PJ, Nowak IA, Mooney RA. Interleukin-6 induces cellular insulin resistance in hepatocytes. Diabetes. 2002;51:3391–3399. - PubMed
-
- Rui L, Fisher TL, Thomas J, White MF. Regulation of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling by proteasome-mediated degradation of insulin receptor substrate-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:40362–40367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

