Rescue of "crippled" germinal center B cells from apoptosis by Epstein-Barr virus
- PMID: 16076866
- PMCID: PMC1895254
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2341
Rescue of "crippled" germinal center B cells from apoptosis by Epstein-Barr virus
Abstract
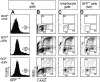
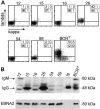
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is associated with B-cell lymphomas such as Hodgkin lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, and post-transplantation lymphoma, which originate from clonal germinal center (GC) B cells. During the process of somatic hypermutation, GC B cells can acquire deleterious or nonsense mutations in the heavy and light immunoglobulin genes. Such mutations abrogate the cell surface expression of the B-cell receptor (BCR), which results in the elimination of these nonfunctional B cells by immediate apoptosis. EBV encodes several latent genes, among them latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) and LMP2A, which are regularly expressed in EBV-positive Hodgkin lymphoma and posttransplantation lymphomas. Since LMP1 and LMP2A mimic the function of 2 key receptors on B cells, CD40 and BCR, respectively, we wanted to learn whether EBV infection can rescue proapoptotic GC B cells with crippling mutations in the heavy chain immunoglobulin locus from apoptosis. We show here that BCR-negative GC B cells readily enter the cell cycle upon infection with EBV in vitro and yield clonal lymphoblastoid cell lines that are incapable of expressing a functional BCR because the rearranged and formerly functional heavy chain immunoglobulin alleles carry deleterious mutations. Our findings imply an important role for EBV in the process of lymphomagenesis in certain cases of Hodgkin lymphoma and posttransplantation lymphomas.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transformation of BCR-deficient germinal-center B cells by EBV supports a major role of the virus in the pathogenesis of Hodgkin and posttransplantation lymphomas.Blood. 2005 Dec 15;106(13):4345-50. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2342. Epub 2005 Aug 30. Blood. 2005. PMID: 16131568
-
Epstein-Barr virus infection in vitro can rescue germinal center B cells with inactivated immunoglobulin genes.Blood. 2005 Dec 15;106(13):4249-52. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2327. Epub 2005 Aug 25. Blood. 2005. PMID: 16123211
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive lymphoproliferations in post-transplant patients show immunoglobulin V gene mutation patterns suggesting interference of EBV with normal B cell differentiation processes.Eur J Immunol. 2003 Jun;33(6):1593-602. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323765. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12778477
-
Molecular biology of Hodgkin's and Reed/Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's lymphoma.Int J Cancer. 2006 Apr 15;118(8):1853-61. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21716. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16385563 Review.
-
B Cell Differentiation and the Origin and Pathogenesis of Human B Cell Lymphomas.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2865:1-30. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4188-0_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39424718 Review.
Cited by
-
EBNA2-deleted Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) isolate, P3HR1, causes Hodgkin-like lymphomas and diffuse large B cell lymphomas with type II and Wp-restricted latency types in humanized mice.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Jun 15;16(6):e1008590. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008590. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32542010 Free PMC article.
-
A Mouse Model to Study the Pathogenesis of γ-herpesviral Infections in Germinal Center B Cells.Cells. 2023 Dec 6;12(24):2780. doi: 10.3390/cells12242780. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132100 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic approaches to investigate gammaherpesvirus biology and associated tumorigenesis.Adv Virus Res. 2021;109:201-254. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Adv Virus Res. 2021. PMID: 33934828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
beta1 integrin expression increases susceptibility of memory B cells to Epstein-Barr virus infection.J Virol. 2010 Jul;84(13):6667-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02675-09. Epub 2010 Apr 28. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20427540 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the Epstein Barr virus to the molecular pathogenesis of Hodgkin lymphoma.J Clin Pathol. 2007 Dec;60(12):1342-9. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2007.050146. J Clin Pathol. 2007. PMID: 18042690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu YJ, Joshua DE, Williams GT, Smith CA, Gordon J, MacLennan IC. Mechanism of antigen-driven selection in germinal centres. Nature. 1989;342: 929-931. - PubMed
-
- Kraus M, Alimzhanov MB, Rajewsky N, Rajewsky K. Survival of resting mature B lymphocytes depends on BCR signaling via the Igalpha/beta heterodimer. Cell. 2004;117: 787-800. - PubMed
-
- Marafioti T, Hummel M, Foss HD, et al. Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells represent an expansion of a single clone originating from a germinal center B-cell with functional immunoglobulin gene rearrangements but defective immunoglobulin transcription. Blood. 2000;95: 1443-1450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

