Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors
- PMID: 16056220
- PMCID: PMC1464427
- DOI: 10.1038/nature03959
Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors
Erratum in
- Nature. 2006 May 4;441(7089):120. Ho, Chun He [corrected to Ho, Chun Heen]
Abstract
The proliferation of large-scale DNA-sequencing projects in recent years has driven a search for alternative methods to reduce time and cost. Here we describe a scalable, highly parallel sequencing system with raw throughput significantly greater than that of state-of-the-art capillary electrophoresis instruments. The apparatus uses a novel fibre-optic slide of individual wells and is able to sequence 25 million bases, at 99% or better accuracy, in one four-hour run. To achieve an approximately 100-fold increase in throughput over current Sanger sequencing technology, we have developed an emulsion method for DNA amplification and an instrument for sequencing by synthesis using a pyrosequencing protocol optimized for solid support and picolitre-scale volumes. Here we show the utility, throughput, accuracy and robustness of this system by shotgun sequencing and de novo assembly of the Mycoplasma genitalium genome with 96% coverage at 99.96% accuracy in one run of the machine.
Figures
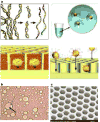
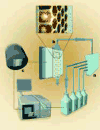
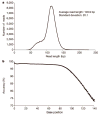
Comment in
-
Genomics: massively parallel sequencing.Nature. 2005 Sep 15;437(7057):326-7. doi: 10.1038/437326a. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16163333 No abstract available.
-
Massively parallel ("next-generation") DNA sequencing.Clin Chem. 2015 Jul;61(7):997-8. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2014.237461. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Clin Chem. 2015. PMID: 25922443 Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Genomics: massively parallel sequencing.Nature. 2005 Sep 15;437(7057):326-7. doi: 10.1038/437326a. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16163333 No abstract available.
-
Massively parallel ("next-generation") DNA sequencing.Clin Chem. 2015 Jul;61(7):997-8. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2014.237461. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Clin Chem. 2015. PMID: 25922443 Review. No abstract available.
-
The complete genome of an individual by massively parallel DNA sequencing.Nature. 2008 Apr 17;452(7189):872-6. doi: 10.1038/nature06884. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18421352
-
A method for parallel, automated, thermal cycling of submicroliter samples.Genome Res. 2001 Mar;11(3):441-7. doi: 10.1101/gr.gr1644r. Genome Res. 2001. PMID: 11230168 Free PMC article.
-
The use of capillary electrophoresis for DNA polymorphism analysis.Mol Biotechnol. 2003 May;24(1):41-68. doi: 10.1385/MB:24:1:41. Mol Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 12721495 Review.
Cited by
-
Introduction to Integrated Proteogenomic Pipeline for Dealing with Pathogenic Missense SNPs.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2859:93-107. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4152-1_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39436598
-
Evolutionary change driven by metal exposure as revealed by coding SNP genome scan in wild yellow perch (Perca flavescens).Ecotoxicology. 2013 Jul;22(5):938-57. doi: 10.1007/s10646-013-1083-8. Epub 2013 May 31. Ecotoxicology. 2013. PMID: 23722603
-
Comparison of sequencing platforms for single nucleotide variant calls in a human sample.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55089. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055089. Epub 2013 Feb 6. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23405114 Free PMC article.
-
SNP detection from de novo transcriptome sequencing in the bivalve Macoma balthica: marker development for evolutionary studies.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052302. Epub 2012 Dec 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300636 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Genome Sequence of Paenibacillus strain Y4.12MC10, a Novel Paenibacillus lautus strain Isolated from Obsidian Hot Spring in Yellowstone National Park.Stand Genomic Sci. 2012 Jul 30;6(3):381-400. doi: 10.4056/sigs.2605792. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Stand Genomic Sci. 2012. PMID: 23408395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prober JM, et al. A system for rapid DNA sequencing with fluorescent chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. Science. 1987;238:336. - PubMed
-
- NIH News Release, October 14, 2004, http://www.genome.gov/12513210
-
- Nyren P, Pettersson B, Uhlen M. Solid phase DNA minisequencing by an enzymatic luminometric inorganic pyrophosphate detection assay. Anal Biochem. 1993;208:171. - PubMed
-
- Ronaghi M, et al. Real-time DNA sequencing using detection of pyrophosphate release. Anal Biochem. 1996;242:84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
