I{kappa}B kinase (IKK){beta}, but not IKK{alpha}, is a critical mediator of osteoclast survival and is required for inflammation-induced bone loss
- PMID: 15897281
- PMCID: PMC2212920
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20042081
I{kappa}B kinase (IKK){beta}, but not IKK{alpha}, is a critical mediator of osteoclast survival and is required for inflammation-induced bone loss
Abstract
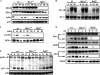
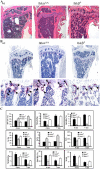
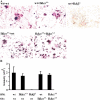
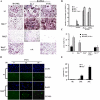
Transcription factor, nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB), is required for osteoclast formation in vivo and mice lacking both of the NF-kappaB p50 and p52 proteins are osteopetrotic. Here we address the relative roles of the two catalytic subunits of the IkappaB kinase (IKK) complex that mediate NF-kappaB activation, IKKalpha and IKKbeta, in osteoclast formation and inflammation-induced bone loss. Our findings point out the importance of the IKKbeta subunit as a transducer of signals from receptor activator of NF-kappaB (RANK) to NF-kappaB. Although IKKalpha is required for RANK ligand-induced osteoclast formation in vitro, it is not needed in vivo. However, IKKbeta is required for osteoclastogenesis in vitro and in vivo. IKKbeta also protects osteoclasts and their progenitors from tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis, and its loss in hematopoietic cells prevents inflammation-induced bone loss.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NF-kappaB p50 and p52 expression is not required for RANK-expressing osteoclast progenitor formation but is essential for RANK- and cytokine-mediated osteoclastogenesis.J Bone Miner Res. 2002 Jul;17(7):1200-10. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.7.1200. J Bone Miner Res. 2002. PMID: 12096833
-
Expression of either NF-kappaB p50 or p52 in osteoclast precursors is required for IL-1-induced bone resorption.J Bone Miner Res. 2003 Feb;18(2):260-9. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.2.260. J Bone Miner Res. 2003. PMID: 12568403
-
Activin A stimulates IkappaB-alpha/NFkappaB and RANK expression for osteoclast differentiation, but not AKT survival pathway in osteoclast precursors.J Cell Biochem. 2003 Sep 1;90(1):59-67. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10613. J Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12938156
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10837071 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-canonical NF-κB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis: Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde?Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jan 28;17(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0527-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25774937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin-reuptake inhibitors act centrally to cause bone loss in mice by counteracting a local anti-resorptive effect.Nat Med. 2016 Oct;22(10):1170-1179. doi: 10.1038/nm.4166. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 27595322 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclastogenesis in periodontal diseases: Possible mediators and mechanisms.J Oral Biosci. 2020 Jun;62(2):123-130. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 17. J Oral Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32081710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cartilage homeostasis in health and rheumatic diseases.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):224. doi: 10.1186/ar2592. Epub 2009 May 19. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19519926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective protein/cathepsin A down-regulates osteoclastogenesis by associating with and degrading NF-kappaB p50/p65.J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(1):46-56. doi: 10.1007/s00774-008-0017-7. Epub 2008 Dec 5. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009. PMID: 19066718
References
-
- Karsenty, G., and E.F. Wagner. 2002. Reaching a genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev. Cell. 2:389–406. - PubMed
-
- Manolagas, S.C., and R.L. Jilka. 1995. Bone marrow, cytokines, and bone remodeling. Emerging insights into the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:305–311. - PubMed
-
- Suda, T., N. Takahashi, N. Udagawa, E. Jimi, M.T. Gillespie, and T.J. Martin. 1999. Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr. Rev. 20:345–357. - PubMed
-
- Kong, Y.Y., H. Yoshida, I. Sarosi, H.L. Tan, E. Timms, C. Capparelli, S. Morony, A.J. Oliveira-dos-Santos, G. Van, A. Itie, et al. 1999. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 397:315–323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

