Cross-host evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in palm civet and human
- PMID: 15695582
- PMCID: PMC548959
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409608102
Cross-host evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in palm civet and human
Abstract
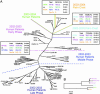
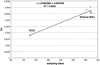
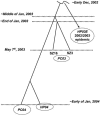
The genomic sequences of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses from human and palm civet of the 2003/2004 outbreak in the city of Guangzhou, China, were nearly identical. Phylogenetic analysis suggested an independent viral invasion from animal to human in this new episode. Combining all existing data but excluding singletons, we identified 202 single-nucleotide variations. Among them, 17 are polymorphic in palm civets only. The ratio of nonsynonymous/synonymous nucleotide substitution in palm civets collected 1 yr apart from different geographic locations is very high, suggesting a rapid evolving process of viral proteins in civet as well, much like their adaptation in the human host in the early 2002-2003 epidemic. Major genetic variations in some critical genes, particularly the Spike gene, seemed essential for the transition from animal-to-human transmission to human-to-human transmission, which eventually caused the first severe acute respiratory syndrome outbreak of 2002/2003.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular evolution analysis and geographic investigation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in palm civets at an animal market and on farms.J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(18):11892-900. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.18.11892-11900.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16140765 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV infection in a restaurant from palm civet.Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Dec;11(12):1860-5. doi: 10.3201/eid1112.041293. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16485471 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways of cross-species transmission of synthetically reconstructed zoonotic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(17):8721-32. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00818-08. Epub 2008 Jun 25. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18579604 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiology, evolution and phylogeny of SARS coronavirus.Infect Genet Evol. 2019 Jul;71:21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Infect Genet Evol. 2019. PMID: 30844511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV and emergent coronaviruses: viral determinants of interspecies transmission.Curr Opin Virol. 2011 Dec;1(6):624-34. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.012. Curr Opin Virol. 2011. PMID: 22180768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emergence of SARS and COVID-19 and preparedness for the next emerging disease X.Front Med. 2024 Feb;18(1):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s11684-024-1066-6. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Front Med. 2024. PMID: 38561562 Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 outbreak: role of viral proteins and genomic diversity in virus infection and COVID-19 progression.Virol J. 2024 Mar 27;21(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02342-w. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38539202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of receptors in the cross-species spread of coronaviruses infecting humans and pigs.Arch Virol. 2024 Jan 24;169(2):35. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05956-7. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 38265497 Review.
-
Global Emergence of SARS-CoV2 Infection and Scientific Interventions to Contain its Spread.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024;25(4):307-325. doi: 10.2174/0113892037274719231212044235. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024. PMID: 38265408 Review.
-
Absence of Coronavirus RNA in Faecal Samples from Wild Primates in Gabon, Central Africa.Pathogens. 2023 Oct 23;12(10):1272. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12101272. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37887788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ksiazek, T. G., Erdman, D., Goldsmith, C. S., Zaki, S. R., Peret, T., Emery, S., Tong, S., Urbani, C., Comer, J. A., Lim, W., et al. (2003) N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1953-1966. - PubMed
-
- Drosten, C., Gunther, S., Preiser, W., van der Werf, S., Brodt, H. R., Becker, S., Rabenau, H., Panning, M., Kolesnikova, L., Fouchier, R. A., et al. (2003) N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1967-1976. - PubMed
-
- Rota, P. A., Oberste, M. S., Monroe, S. S., Nix, W. A., Campagnoli, R., Icenogle, J. P., Penaranda, S., Bankamp, B., Maher, K., Chen, M. H., et al. (2003) Science 300, 1394-1399. - PubMed
-
- Marra, M. A., Jones, S. J., Astell, C. R., Holt, R. A., Brooks-Wilson, A., Butterfield, Y. S., Khattra, J., Asano, J. K., Barber, S. A., Chan, S. Y., et al. (2003) Science 300, 1399-1404. - PubMed
-
- Guan. Y., Zheng, B. J., He, Y. Q., Liu, X. L., Zhuang, Z. X., Cheung, C. L., Luo, S. W., Li, P. H., Zhang, L. J., Guan, Y. J., et al. (2003) Science 302, 276-278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

